Used to be Every other Box Find out about Justified?
The Biology In the back of Mite Switch Between Hives
How A lot Mite Immigration In fact Happens?
How Do the Mites Get Transferred?
How Necessary is the Drifting of Drones?
How A lot Go with the flow is There of Employee Bees?
How Necessary are the Guard Bees?
Do Mites and Viruses Purpose Larger Drifting?
Robbing vs. “Abnormal” Drifting
How Some distance Can Mites Hitchike a Trip?
A Find out about on Bee Go with the flow and Mite Immigration
Phase 1
Randy Oliver
ScientificBeekeeping.com
First Printed in ABJ in February 2023
Many beekeepers whinge about unexpected late-summer spikes of their varroa counts, blaming them on mites immigrating into their hives from different colonies locally. When my sons and I suspected that this was once happening in some our personal yards, I made up our minds to run a box find out about to determine precisely what was once taking place.
INTRODUCTION
It calls for human shipping to transport the varroa mite throughout geographical boundaries, however to the dismay of beekeepers, as soon as offered into a rustic, the mite can unfold all of a sudden to all colonies within the area. This invasiveness is in large part because of the herbal glide of bees, which additionally ends up in the sporting of mites from hive to hive. I wrote about what was once then identified about mite glide again within the spring of 2018, and recommend that in the event you’re on this matter that you just first overview my two articles at the matter [[1]].
SO WAS ANOTHER FIELD STUDY ON MITE DRIFT JUSTIFIED?
To respond to that query, let’s check out knowledge from Ritter in Germany, taken again in 1987 [[2]]. The paper was once in German, however price translating. Ritter arrange two separate apiaries of 16 mite-free colonies — one within the foothills of the Black Wooded area in a space with low colony density and the opposite within the Rhine simple with a large number of closely infested colonies in the surroundings, after which tracked the infestation charges of the bees and brood within the experimental hives through the years. His effects showed that having heavily-infested colonies locally could make a heckuva distinction (Determine 1).
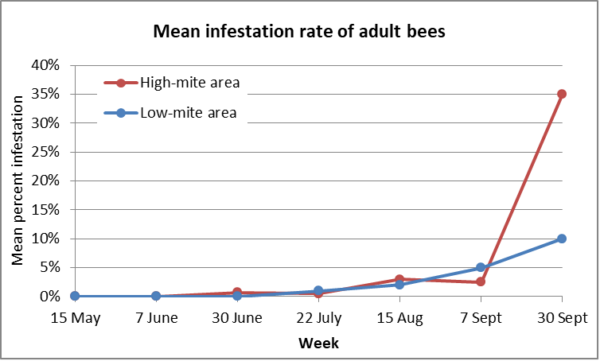
Fig. 1. Of passion is how lengthy it took for the impact to turn within the mite washes. At an infestation price of 35%, that will be 110 mites in a wash of a part cup of bees! Facet notice: Again then the advice in Germany was once to make use of gas for acting mite washes. I guess that they have been cautious with their people who smoke!
However was once the above unexpected spike within the infestation price because of a unexpected inflow of mites in September? Check out Determine 2.
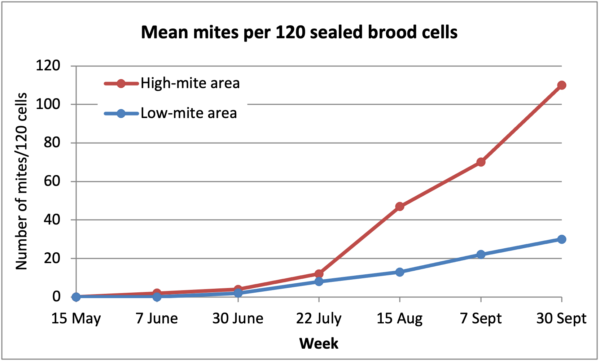
Fig. 2. Apparently that the affect of mite immigration in reality began to happen lengthy prior to September. The plain “unexpected” spike as indicated by means of mite washes will have in reality been because of an exponential build up in mite emergence in September, right into a lowering choice of grownup bees within the hives. This will provide an explanation for why even beekeepers who’re tracking by way of mite washes would possibly nonetheless get shocked!
Sensible utility: Ritter’s box knowledge indubitably means that mite immigration from different colonies locally can have an effect on the velocity of mite buildup in a single’s personal hives. So I sought after to dive deeper.
With the intention to higher perceive this phenomenon, I changed my mite style [[3]] to run some simulations (after first confirming that the style may just produce ends up in the ballpark of Ritter’s knowledge). Let’s first check out the estimations of main points of varroa buildup through the years in an untreated colony headed in opposition to cave in in October (Determine 3).
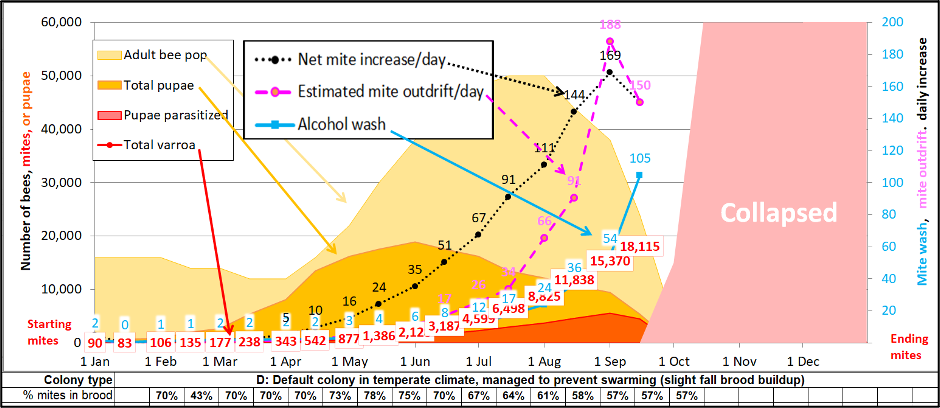
Fig. 3. Permit me to make use of the simulation above to introduce you to the concept that of the “Mite Manufacturing facility.” I added further plots for day by day quantity of mite build up, in addition to for the estimated quantity of mite exodus on outgoing bees. Learn under for explanations.
By the point an untreated, nonresistant Mite Manufacturing facility about to cave in:
- It’ll in most cases include round 15,000 mites in overall.
- The above quantity will probably be expanding at a internet build up of about 150 mites in step with day.
- And because of the fast lifespan of summer time bees, above that quantity, there can be over 150 mites hitching a last journey out of the colony on a daily basis [[4]].
Sadly, there are too many variables for the style to are expecting the choice of the ones exiting mites fortunate sufficient to be carried to any other hive. With the above figures in thoughts, you’ll be questioning:
Sensible query: What affect may a Varroa Manufacturing facility locally have upon my well-managed (handled) hives?
To respond to that query, let’s run the similar simulation, however this time with a few efficacious remedies (Determine 4).
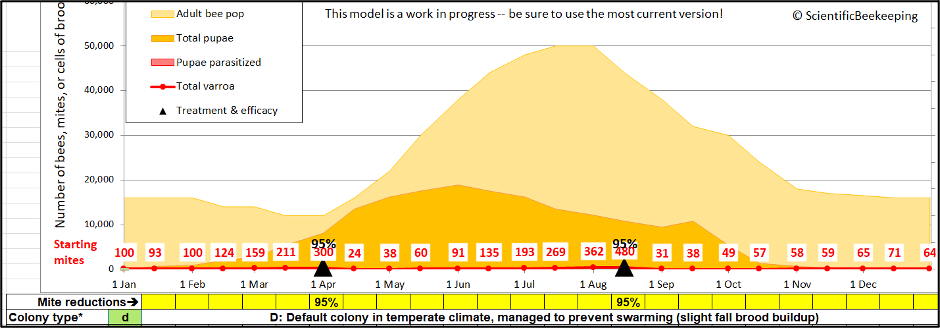
Fig. 4. Similar simulation, however this time handled in April and August, leading to a a long way decrease mite stage in mid-September (round 35). This now offers us two baseline numbers (15,000 and 35) to play with.
Now consider a local through which one out of each ten hives is untreated, whilst the opposite 9 colonies are handled (each and every containing a mean of best 35 mites, as in the second one simulation). Let’s see what occurs if an arbitrary 10% of the 15,000 mites within the untreated colony by hook or by crook arrange to flippantly “diffuse” (by way of bee glide) into the 9 different handled hives (a mean of 165 mites in step with hive)(Determine 5).
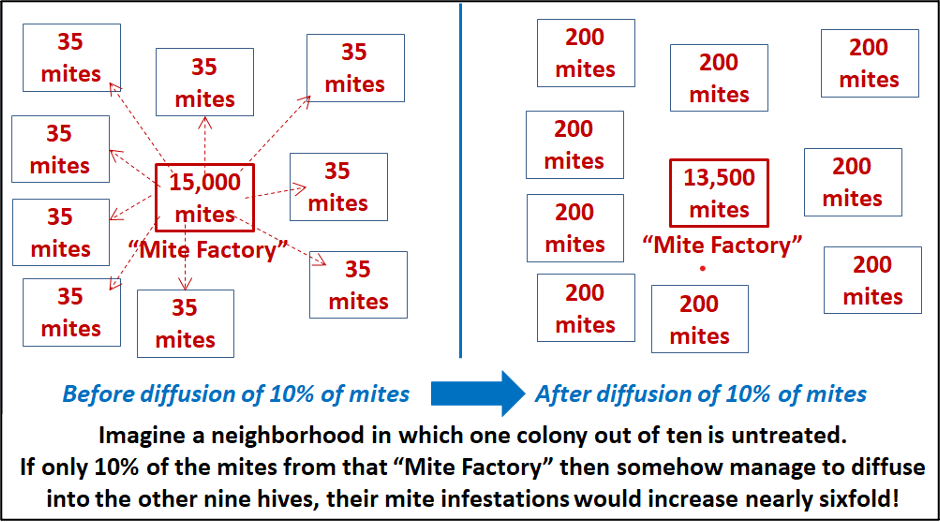
Fig. 5. A unmarried “Mite Manufacturing facility” has the prospective to noticeably reinfest all of the different hives locally after their mid-August remedy (in truth, the distribution of mites would in fact be asymmetric, with some colonies receiving extra mites than others). Believe the impact in case your apiary was once surrounded by means of a lot of “mite factories”!
OK, so mite immigration may just obviously have a noticeable affect in the event you already had your mites properly beneath keep an eye on, however what in the event you have been working slightly at the back of the curve? (Determine 6).
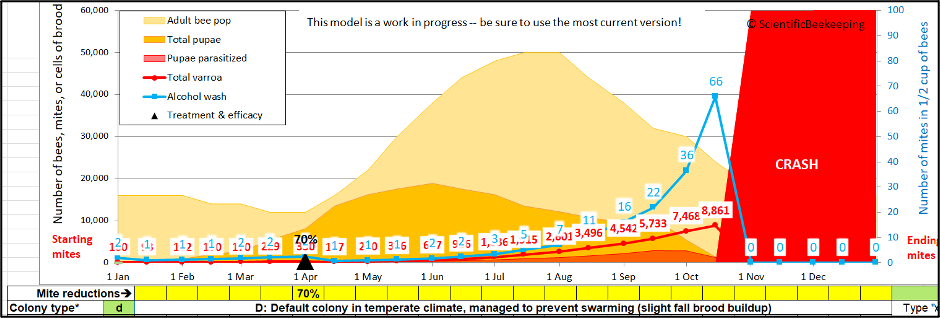
Fig.6. On this simulation of fairly-typical colony control, the efficacy of the April remedy was once best so-so (because of lots of the mites being within the brood). After which the beekeeper hadn’t gotten round to giving an August remedy. Going into September, the simulated colony displays a mite wash depend of 16 — which might be ordinary of “moderate” control practices [[5]]. However the mite inhabitants in that hive would quickly exceed 5000, which means that an immigration of the similar 165 mites as within the earlier situation could be just a drop within the bucket!
Sensible utility: For those who’re no longer staying on most sensible of varroa all season lengthy, it can be a stretch guilty a late-season spike in mite counts upon mite immigration from in different places.
Apparently as although mite immigration may just certainly be a subject for the ones making the hassle to take care of low mite counts. So I felt {that a} box find out about to raised perceive mite immigration in my operation was once justified!
BACKGROUND RESEARCH
The very first thing I need to do when designing a analysis challenge is to determine what’s already identified. For this newsletter, I’ll snip some quotes (with minor paraphrasing and added emphasis) from related publications.
The second one factor is then resolve the explicit questions that I would like to take a look at to reply to — those will probably be my find out about goals (which I can listing under).
THE BIOLOGY BEHIND MITE TRANSFER BETWEEN HIVES
Varroa is an overly a hit parasite, all of a sudden reproducing in its personal host honey bee colony. However for the parasite’s persisted luck, bloodlines of the mite should by hook or by crook “horizontally switch” to different host colonies previous to the dying in their host colony.
To the mites’ nice merit, they’re ready to make use of bees exiting their host colony as an unwitting supply provider that takes them without delay into different colonies inside of flight vary. This hitchhiking no longer best permits varroa to infest newly-established colonies, but additionally to combine their genes amongst neighboring host colonies (which is helping the mite to conform).
HOW MUCH MITE IMMIGRATION ACTUALLY OCCURS?
It takes just a unmarried fertile feminine mite to start out an infestation in a colony. However beekeepers quickly spotted that the stage of mite immigration was once now and again a lot more than that. Following Ritter’s newsletter, in 1988, German researchers Sakofski and Koeniger wrote a bankruptcy known as “Herbal switch of Varroa jacobsoni amongst honeybee colonies in autumn” [[6]]. And in 1990 [[7]] they once more showed that colonies from which varroa were eradicated by means of remedy may well be reinvaded by means of the mite, particularly all over past due summer time and fall. After which in 1992Greatti [[8]] printed knowledge indicating surprising quantities of mite invasion happening in his monitored colonies in Italy. Those findings have been adopted by means of different analysis, significantly that of Frey [[9]], who discovered that mites may just glide for a substantial distance. I’ve summarize the above find out about effects in the past [[10]], however would they observe to my places in California?
Sensible utility: There’s without a doubt that mite migration between colonies can happen, and that it may be considerable. The questions for beekeepers then are precisely how and why it happens, how a lot immigration a colony can in reality obtain, and is there the rest that we will be able to do to cut back it.
Find out about Purpose #1: To resolve the volume of mite immigration that in reality takes position in past due summer time and fall the place I stay my bees.
Find out about Purpose #2: To resolve whether or not that mite immigration is stable or episodic.
Find out about Purpose #3: To resolve whether or not all hives endure similarly from mite immigration, or whether or not some are extra horny or receptive than others.
HOW DO THE MITES GET TRANSFERRED?
Because the mites rely on bees to hold them to different colonies, it’s essential to grasp this facet. Greatti [[11]] indexed the 3 major strategies through which the mite manages to disperse from one colony to any other:
- By way of the drifting of drones, that are identified to glide freely between hives.
- By way of the drifting of employee bees — which can have a tendency to “diffuse” mites from colonies with excessive infestation to these with low infestation.
- By way of the robbing of colonies weakened by means of heavy infestation.
HOW IMPORTANT IS THE DRIFTING OF DRONES?
A contemporary find out about by means of Mortensen [[12]] showed that drones do raise mites. It’s widely known that drones have a tendency to glide to different hives. That stated, Greatti, in conjunction with quantifying the real quantity of mite immigration that would happen, examined whether or not striking drone excluders over the entrances of colonies would scale back immigration. He discovered that it didn’t.
Sensible utility: Even if drones do a large number of drifting, they won’t give a contribution a lot to mite glide, and because there are only a few drones in our colonies in past due summer time, I didn’t pursue the drone issue.
HOW MUCH DRIFT IS THERE OF WORKER BEES?
There were numerous research indicating that there can also be substantial glide of employee bees, particularly in crowded apiaries, the place greater than part the employees in a colony would possibly glide at a while of their lives to different hives [[13]].
However how in regards to the moderately unexpected disappearance of the bees from a hive because it collapses from the varroa-virus advanced. Do the ones bees simply “disappear,” or do they finally end up in different colonies?
Find out about Purpose #4: To resolve the share of staff that glide from collapsing colonies into different hives.
HOW IMPORTANT ARE THE GUARD BEES?
There’s any other facet of employee glide but even so bees simply getting misplaced — to go into a international hive, they first want to get previous the guards. Since I’ve lengthy decided on for “mild” inventory, I’ve puzzled whether or not I’ve additionally been inadvertently deciding on for bloodlines whose guards may well be extra permissive to drifted bees making an attempt to go into their hive (Determine 7).
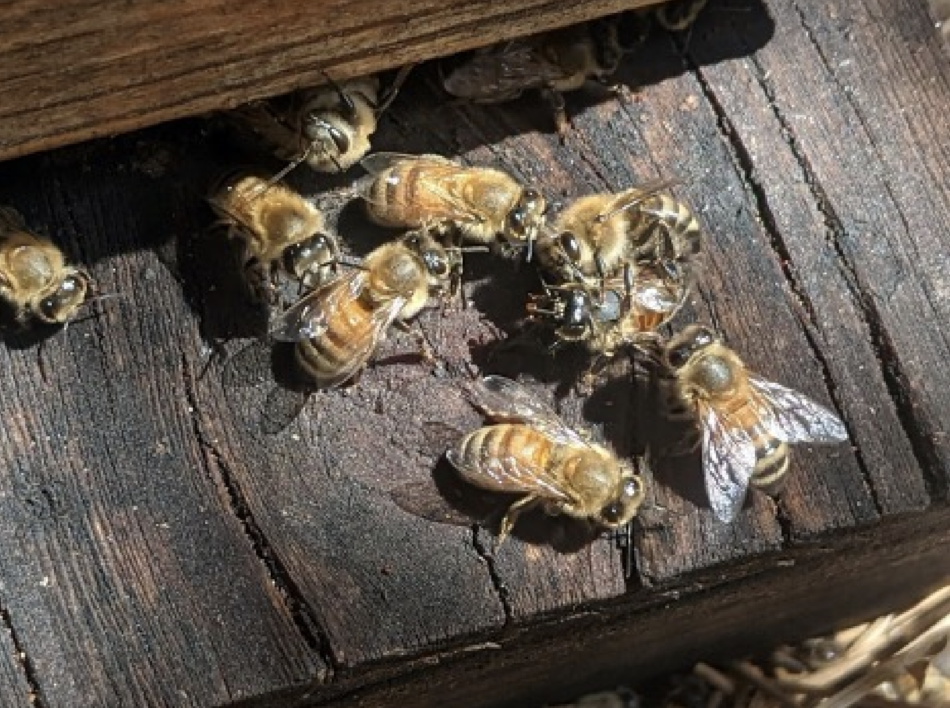

Fig. 7. Even if we breed for gentleness, I regularly practice guards doing a just right task at protecting the doorway towards intruders.
In 2017 Bordier [[14]] used video cameras to trace tagged bees on the entrances of monitored hives (Determine 8).

Fig. 8. I visited the INRA analysis facility in 2018, and snapped this image of some of the video front tracking gadgets that they have been the use of.
Bordier concluded that (I’ve boldfaced the highlights):
Drifting habits is a end result of orientation mistakes, and in addition is dependent upon the acceptance stage of the brand new host colony… adjustments in drifting depth are most probably the results of an build up in colony acceptance. In customary prerequisites, best 3.5 % of incoming bees are checked by means of guard bees, however this permissiveness adjustments consistent with season, density of bees and nectar and pollen sources— the acceptance ranges of colonies build up when nectar waft is ample however lower all over dearth sessions.
Sensible utility: So I’m nonetheless no longer transparent at the significance of the guards in combating mite immigration. Of passion is the discovering by means of Cappa [[15]] that guard bees mount a better protection towards drifting bees which have been parasitized by means of a mite (how a lot may this play into “mite resistance” of a colony?). Distinction that discovering to that of Geffre [[16]], who “discovered that IAPV-inoculated bees have been considerably much more likely to be authorized by means of the guards on the colony front than have been…controls.”
We clearly nonetheless have a lot to be informed about guarding and drifting. I arrange my find out about so that we might best get better drifted bees that made it previous the guards at the touchdown board.
DO MITES AND VIRUSES CAUSE INCREASED DRIFTING?
It’s widely known to biologists that any choice of parasites can exchange the behaviors in their hosts to be able to impact higher transmission [[17]]. In order proposed by means of DeGrandi-Hoffman [[18]] in 2017:
We hypothesize that rigidity from parasitism and virus an infection mixed with results that viruses have on cognitive serve as would possibly give a contribution to forager glide and mite and virus dispersal.
So is there proof for greater glide from colonies present process cave in? In 1991 Sakofski [[19]] discovered that:
By way of evaluating numbers of bees drifting from extremely infested and noninfested small colonies it may well be proven that infested colonies drifted extra continuously. The invasion of mites into bee colonies was once monitored all over a duration from spring to autumn. All colonies confirmed low values of mite inflow which greater significantly on the finish of July and remained excessive till the start of October. Person values differed over broad levels that are more likely to be brought about by means of theft.
However in 2000, Neuman [[20]], even if discovering considerable glide of staff and drones, did no longer discover a correlation between employee bee glide and varroa infestation
Goodwin [[21]] ran a box trial in New Zealand wrote in 2006, through which six of 8 high-mite colonies with marked bees collapsed and were given robbed out. In spite of that:
The common share of bees drifting from untreated hives infested with varroa into neighboring handled hives didn’t exceed 3%. There have been no vital variations between the share of drifting bees from the varroa-infested colonies and the handled colonies at any level all the way through the trial. This implies that the reinfestation of handled colonies does no longer predominantly outcome from heavy varroa infestations inflicting employee bees to glide to different colonies, greater than they typically do in almost varroa-free colonies.
After which in 2014 the idea that highly-infested bees have been predisposed to glide was once given wind by means of Cervo [[22]]:
At low mite abundance, mites keep throughout the colony the place they’re born and advertise their replica by means of driving nurses. This desire guarantees that mites are briefly transferred to any other host larva inside of the similar colony the place they may be able to reproduce. When mite abundance will increase throughout the colony, the loss of variations in chemical cues between nurses and foragers more than likely does no longer permit mites to discriminate between bees with other duties and reasons mites to journey on either one of them…. by means of driving each nestmate foragers and international [robbers], mites build up their likelihood of leaving the exploited colonies. An infested colony, step by step weakened by means of parasites and mite-transmitted sicknesses, in the end turns into a very simple goal for robbing foragers from international colonies; those robber international bees may constitute very good vectors to without delay switch mites from the previous exploited beehive to a brand new one.
This speculation in an instant received traction, and by means of 2017 the time period “Mite Bombs” was once being thrown about, even if with little supportive proof. And it was once a foggy perception – no longer obviously differentiating the day-by-day “diffusive” mite glide from high-mite or collapsing colonies, as opposed to the unexpected and temporary direct switch of mites all over robbing occasions that would possibly happen all over the cave in of a colony.
In 2017 Bordier [[23]] discovered that:
Roughly 10 % of our tracked bees drifted right into a international colony. The drifting incidence was once influenced by means of the colony’s location in house however no longer by means of N. ceranae parasitism.
There have been no vital variations between the share of drifting bees from the varroa-infested colonies and the keep an eye on colonies at any level all the way through the find out about. This implies that the reinfestation of handled colonies does no longer predominantly outcome from heavy varroa infestations inflicting employee bees to glide to different colonies, greater than they typically do in almost varroa-free colonies….The standard stage of glide in apiaries will, on the other hand, unfold varroa from untreated to handled colonies.
And in 2019 Peck and Seeley [[24]] discovered that:
We noticed no indications that drifting of bees from the mite donor colonies into the mite receiver colonies greater because the mite ranges within the mite donor colonies greater.
Sensible utility: As horny as a virus-induced build up in drifting habits speculation is, there are up to now conflicting findings (Determine 9).
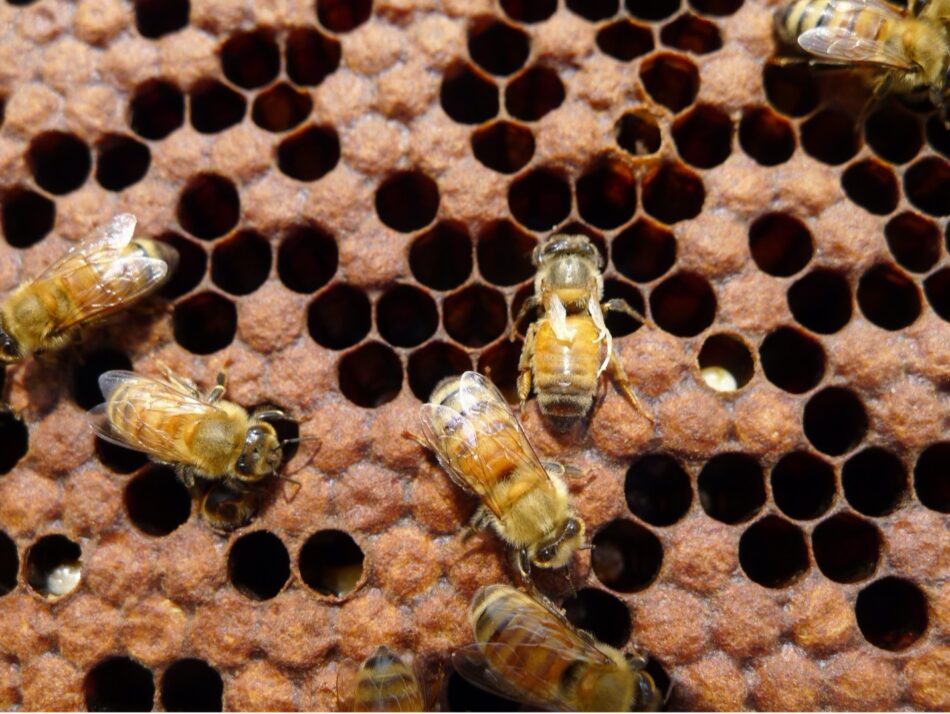

Fig. 9. It’s simple to spot an unlucky employee that suffered from this sort of excessive an infection price of DWV that its wings may just no longer broaden. However you’ll safely suppose that each employee on this photograph is inflamed with DWV to some degree, as evidenced by means of the death brood. However does the varroa-DWV advanced purpose those inflamed bees to glide at a better price?
Find out about Purpose #5: To resolve whether or not increased varroa/virus ranges build up bee glide in my very own operation.
ROBBING VS. “ORDINARY” DRIFTING
We’ve now labored our manner down as to whether mite immigration (a) is essentially because of the “extraordinary” glide of bees from hive to hive (which I name “mite diffusion” because the internet impact will probably be to transport mites from colonies with excessive mite focus to these with decrease focus), or (b) is basically from robbing bees sporting mites again from varroa-weakened hives. Such robbing may well be surreptitious (and not noted by means of the beekeeper) or “overt” (simply seen on the front when a collapsing colony will get mobbed by means of robbers) (Determine 10).
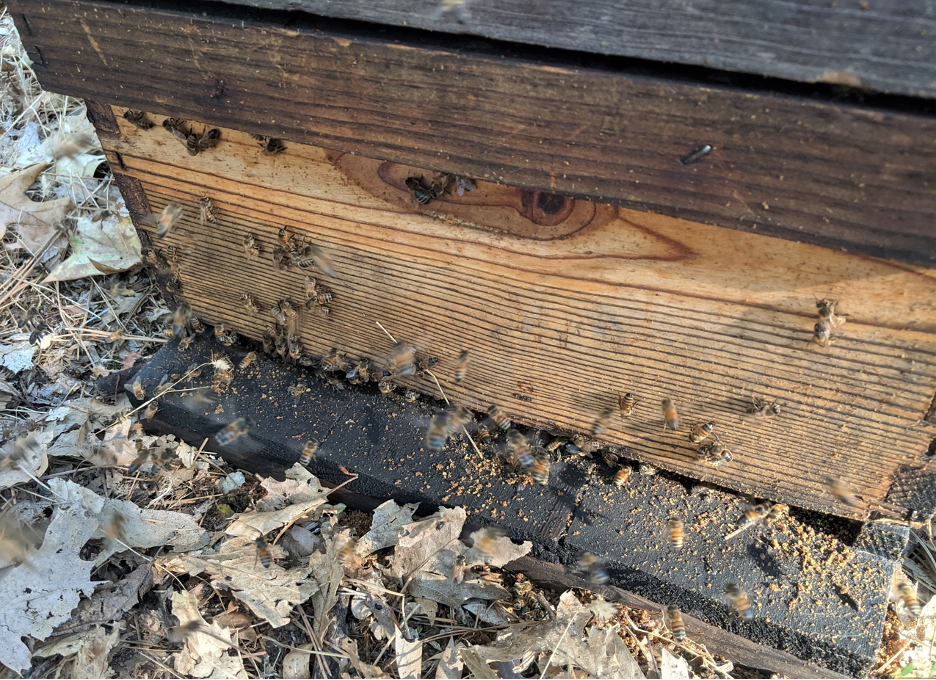

Fig. 10. The abnormal job on the front, coupled with the particles at the touchdown board signifies that this dwindled colony is getting robbed. I believe that during our location, maximum mite immigration because of robbing may well be from the surreptitious robbing that takes position all over nectar flows, when there are few guards on the front.
Peck and Seeley [[25]] regarded into mite glide all over robbing occasions happening in Ithaca, NY past due within the season:
Our knowledge additionally disclose that the colloquial terminology for [heavily infested] colonies—“mite bombs”—does no longer appropriately describe the mechanisms of intercolony mite transmission that we seen on this find out about. We noticed no unexpected “explosion” of mite-carrying bees from unwell colonies to each and every of the wholesome colonies by way of employee drifting. Certainly, we discovered that few mites handed from the closely infested (MDC) colonies to the weakly infested (MRC) colonies via both employee glide (most commonly to within sight colonies) or drone glide. It was once best when the MDCs have been weakened such a lot that they changed into impossible to resist robbing goals that mites handed in massive numbers from the MDCs to the MRCs.
Sensible utility: The mites in a colony this is being robbed as it’s present process cave in (whilst there are nonetheless numerous reside mites within the hive) can indubitably hop onto the robbers (which the mites may just simply acknowledge because of their other smell) and get carried again to the robbing colony. However such rapid robbing doesn’t happen in all landscapes — see my ancillary article on this factor.
And in the end, Kulhanek printed a find out about closing 12 months [[26]].
Extra bees from low mite colonies (n= 37) have been detected in receiver apiaries than bees from excessive mite colonies (n= 10). Receiver colony Varroa inhabitants expansion was once related to visitation by means of non-natal bees, however no longer excessive mite bees on my own. In any case, colonies missing robbing monitors skilled quicker Varroa inhabitants expansion than screened neighbors. Effects point out visiting non-natal bees would possibly vector mites to receiver colonies. Those effects don’t fortify the present two main theories relating to mite immigration – the “mite bomb” concept (bees from excessive mite colonies emigrating to collapsing colonies), or the “robbing” concept (natal robbing bees go back house with mites from collapsing colonies).
Sensible utility: Even if mite glide all over rob outs can certainly happen, it can be that mite diffusion because of extraordinary bee glide is also extra essential. Since robbing monitors don’t save you colonies from robbing, Kulhanek’s findings recommend that they’ll cut back bee (and subsequently, mite) glide (teaser: I can quickly be publishing my very own checking out of robbing monitors).
Find out about Purpose #6: To resolve whether or not mite immigration correlates with robbing.
There’s nonetheless another merchandise of passion…
HOW FAR CAN MITES HITCHIKE A RIDE?
A find out about by means of Frey in 2011 [[27]] had a stunning discovering — that mite glide isn’t essentially a serve as of distance, and that there can also be substantial glide even to colonies a mile far away.
Right through the experimental duration, between 85 and 444 mites in step with colony have been offered into the receiver colonies. There have been no vital variations within the invasion charges with regards to the gap between donor and receiver colonies. In overall, 2,029 mites have been discovered within the 10 receiver colonies, however those best correspond to two.5% of the overall mite inhabitants within the donor colonies firstly of the experiment. Because of this the most important a part of the preliminary V. destructor inhabitants died along with the collapsed host colonies…From a sensible viewpoint shall we display that extremely infested honey bee colonies provide a considerable chance to already handled colonies as much as distances of one.5 km [roughly a mile] away.
Kulhanek [[28]] seen considerable glide between hives in the similar backyard, however her cameras seen best 47 marked bees (out of roughly 32,000 painted) drifting to receiver hives a part mile or additional far away.
Sensible utility: Frey’s discovering of the loss of correlation between mite glide and distance was once one thing that I sought after to check in my house backyard.
Find out about Purpose #7: To resolve the gap that bees can glide from collapsing colonies.
Find out about Purpose #8: To resolve how the velocity of glide to within sight hives compares to that to hives extra far away.
NEXT MONTH
Within the subsequent installment I’ll display we arrange our box find out about to be able to in finding out the solutions to the indexed goals. Keep tuned!
ACKNOWLEGEMENTS
Due to Peter Borst and Dianne Behnke for his or her help with discovering and scanning copies of previous analysis papers.
CITATIONS AND NOTES
[1] The Varroa Drawback: Bee Go with the flow and Mite Dispersal, Portions 16 a & b:
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/the-varroa-problem-part-16a/
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/the-varroa-problem-part-16b/
[2] Ritter, W., & E Leclercq (1987). Entwicklung der Bienen-und Varroa-population in Gebieten mit unterschiedlichen Möglichkeiten der Reinvasion. Tierärzt Umschau 42: 548-51.
[3] https://scientificbeekeeping.com/scibeeimages/Randys-Varroa-Fashion-V2022-1-1.xlsx
[4] This determine is calculated from the calculated choice of non-returning grownup bees in step with day (because of growing older, getting misplaced, or different reasons), assuming that they’re sporting mites at best 2/3 the infestation price of the employee bees on moderate).
[5] Kulhanek Ok, et al (2021) Survey-derived very best control practices for yard beekeepers make stronger colony well being and cut back mortality. PLoS ONE 16(1): e0245490.
[6] Sakofski, F & N Koeniger (1988) Herbal switch of Varroa jacobsoni amongst honeybee colonies in autumn. In Eu Analysis on Varroatosis Keep an eye on.
[7] Sakofski, F, N Koeniger, S Fuchs (1990). Seasonality of honey bee colony invasion by means of Varroa jacobsoniOud. Apidologie, 21(6), 547-550.
[8] Greatti, M, N Milani, F Nazzi (1992). Reinfestation of an acaricide-treated apiary by means of Varroa jacobsoniOud. Experimental & implemented acarology, 16(4), 279-286.
[9] Frey, E, H Schnell, P Rosenkranz (2011). Invasion of Varroa destructor mites into mite-free honey bee colonies beneath the managed prerequisites of an army coaching space. Magazine of Apicultural Analysis, 50(2), 138-144.
[10] https://scientificbeekeeping.com/the-varroa-problem-part-16b/
[11] Greatti, M (1992) Op. cit.
[12] Mortensen, A, C Jack, J Ellis (2018). The invention of Varroa destructor on drone honey bees, Apis mellifera, at drone congregation spaces. Parasitology Analysis 117(10): 3337-3339.
[13] Pfeiffer, Ok & Ok Crailsheim (1998). Drifting of honeybees. Insectes Sociaux 45(2): 151-167.
[14] Bordier, C, et al (2017) Will have to I keep or must I am going: honeybee drifting behaviour as a serve as of parasitism. Apidologie 48(3): 286–297.
[15] Cappa, F, et al (2016) Bee guards hit upon international foragers with cuticular chemical profiles altered by means of phoretic varroa mites. Magazine of Apicultural Analysis 55(3): 268-277.
[16] Geffre, A, et al (2020). Honey bee virus reasons context-dependent adjustments in host social habits. Lawsuits of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, 117(19): 10406-10413.
[17] Poulin, R (2010) Parasite manipulation of host habits. Advances within the Find out about of Conduct 41: 151-186.
[18] DeGrandi-Hoffman, G, F Ahumada, H Graham (2017). Are dispersal mechanisms converting the host–parasite dating and lengthening the virulence of Varroa destructor (Mesostigmata: Varroidae) in controlled honey bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) colonies? Environmental Entomology 46(4): 737-746.
[19] Sakofski, F (1991) Quantitative investigations on switch of Varroa jacobsoni Oud. In Contemporary analysis on bee pathology. Global symposium of the Global Federation of Beekeepers Associations, Gent (Belgium), 5-7 Sep 1990.
[20] Neumann, P, et al (2000) Colony analysis isn’t suffering from drifting and employee honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) at a efficiency checking out apiary. Apidologie 31: 67–79.
[21] R M Goodwin, et al (2006) Go with the flow of Varroa destructor-infested employee honey bees to neighbouring colonies. Magazine of Apicultural Analysis 45(3): 155-156.
[22] Cervo, R, et al (2014) Top Varroa mite abundance influences chemical profiles of employee bees and mite-host personal tastes. J. Exp. Biol. 217: 2998– 3001.
[23] Bordier, C, (2017) Op. cit.
[24] Peck DT & TD Seeley (2019) Mite bombs or robber lures? The jobs of drifting and robbing in Varroa destructortransmission from collapsing honey bee colonies to their neighbors. PLoS ONE 14(6): e0218392.
[25] Peck DT (2019) op. cit.
[26] Kulhanek, Ok, et al (2021) Sped up Varroa destructor inhabitants expansion in honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies is related to visitation from non-natal bees. Clinical reviews, 11(1): 1-15.
[27] Frey, E (2011) Op. cit.
[28] Kulhanek, Ok (2021) op cit.

