Scientists have used complicated statistical research to evaluate one of the dramatic adjustments within the historical past of visual lifestyles on Earth. On the finish of the Permian, all over a mass extinction tournament there was once a dramatic and in depth faunal turnover between brachiopods and bivalves.
Probably the most greatest crises in Earth’s historical past was once marked by means of a revolution within the shellfish. Brachiopods, often referred to as “lamp shells”, as some genera superficially resembled Roman lamps, have been changed in every single place ecologically by means of the bivalves, reminiscent of clams, mussels and oysters. This came about because of the devastating end-Permian mass extinction which reset the evolution of lifestyles 250 million years in the past.
Analysis performed by means of palaeontologists primarily based in Wuhan (China) and the College of Bristol, has shed new gentle in this a very powerful faunal turnover when ocean ecosystems modified, ultimately taking over a extra fashionable, acquainted construction that also persists these days.

Brachiopods and Bivalves
Lifestyles on land and within the sea is wealthy and paperwork explicit ecosystems. In fashionable oceans, the seabed is ruled by means of animals reminiscent of bivalves, corals, gastropods, crustaceans, marine worms and fishes. Those ecosystems all date again to the Triassic when lifestyles slowly recovered from the “Nice Loss of life”. Right through that disaster, just one in twenty species survived, and there was lengthy debate about how the brand new ecosystems have been built and why some teams survived, and others perished.
Brachiopods have been the dominant shelled animals previous to the extinction. Alternatively, bivalves thrived afterwards, reputedly higher adapting to their new prerequisites.
Lead writer of the learn about revealed in “Nature Communications”, Zhen Guo commented:
“A vintage case has been the substitute of brachiopods by means of bivalves. Palaeontologists used to mention that the bivalves have been higher competition and so beat the brachiopods by hook or by crook all over this disaster time. There is not any doubt that brachiopods have been the most important workforce of shelled animals earlier than the extinction, and bivalves took over after.”
Statistical Bayesian Research
Co-author Joe Flannery-Sutherland added:
“We needed to discover the interactions between brachiopods and bivalves via their lengthy historical past and particularly across the Permian-Triassic handover duration. So, we determined to make use of a computational approach known as Bayesian research to calculate charges of origination, extinction, and fossil preservation, in addition to checking out whether or not the brachiopods and bivalves interacted with each and every different. For instance, did the upward thrust of bivalves motive the decline of brachiopods?”
The researchers discovered that actually each teams shared an identical tendencies in diversification dynamics all the way through the time of worldwide disaster.
This means that those two teams weren’t in reality competing or preying on each and every different. It’s much more likely that those unrelated teams have been responding to an identical exterior drivers reminiscent of fluctuations in sea temperature, oxygen ranges and acidity.
The bivalves ultimately prevailed, and the brachiopods retreated to deeper waters, the place they nonetheless happen, however in a lot decreased numbers.
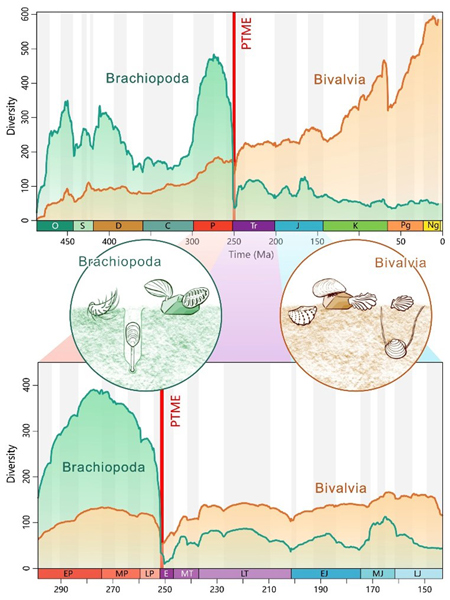
Statistical Research to Get to the bottom of the Brachiopods and Bivalves Faunal Turnover Factor
Professor Zhong-Qiang Chen (China College of Geosciences, Wuhan) defined that it was once very gratifying to peer how fashionable computational ways helped unravel a long-standing factor in palaeontology.
Professor Zhong-Qiang Chen mentioned:
“We all the time concept that the end-Permian mass extinction marked the tip of the brachiopods and that was once that. However it sort of feels that each brachiopods and bivalves have been hit laborious by means of the disaster, and each recovered within the Triassic, however the bivalves may adapt higher to top ocean temperatures. So, this gave them the threshold, and after the Jurassic, they simply rocketed in numbers, and the brachiopods didn’t do a lot.”
Fossils of over 330,000 brachiopods and bivalves have been analysed during this learn about. The Bristol College supercomputer took weeks to crunch all of the numbers. The Bayesian research took into consideration a wide variety of uncertainties and facets of the knowledge to offer a particularly detailed document at the evolutionary adjustments.
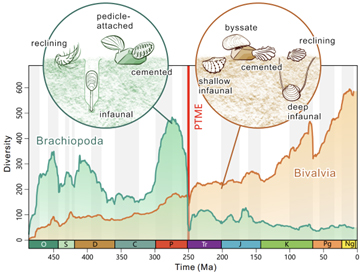
Professor Michael Benton (College of Bristol) concluded:
“The top-Permian mass extinction was once the most important of all time, and it hugely reset evolution. In reality the 50 million years after the disaster, the Triassic, marked a revolution in lifestyles on land and within the sea. Figuring out simply how lifestyles may come again from near-annihilation after which set the root for contemporary ecosystems is without doubt one of the large questions in macroevolution. I’m positive we haven’t stated the ultimate right here regardless that!”
The whole thing Dinosaur recognizes the help of a media unlock from the College of Bristol within the compilation of this text.
The medical paper: “Bayesian analyses point out bivalves didn’t power the downfall of brachiopods following the Permian-Triassic mass extinction” by means of Zhen Guo, Joseph T. Flannery-Sutherland, Michael J. Benton, and Zhong-Qiang Chen revealed in Nature Communications.
Consult with the The whole thing Dinosaur web site: The whole thing Dinosaur.
