The invention of phosphorus in a cloud on the fringe of the Milky Manner has prolonged the area in our galaxy the place existence may well be discovered.
Phosphorus is considered one of six primary components for existence on Earth, in conjunction with nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur (SN: 12/16/22). Till now, it were the one a kind of components lacking from the farthest reaches of our galaxy. Discovering phosphorus that a long way out may just prolong the galaxy’s liveable zone out from its heart by means of more or less 22,000 light-years, researchers reported June 8 at a gathering of the American Astronomical Society in Albuquerque. That during flip may just encourage astronomers to seem within the hinterlands of the Milky Manner for planets and any existence they may harbor.
The crew pointed two radio telescopes at a groovy, dusty gasoline cloud on the fringe of the galaxy. The cloud is a frigid –248° Celsius — an insignificant 25 levels above absolute 0. It sits about 74,000 light-years from the galactic heart, just about triple the space Earth is from the Milky Manner’s core. And it has signatures of phosphorus monoxide and phosphorus mononitride, astrochemist Lilia Koelemay mentioned on the assembly.
Searching for phosphorus in that far-off cloud used to be an extended shot, says astrochemist Lucy Ziurys, Koelemay’s collaborator on the College of Arizona in Tucson. The detail is produced best in supernovas. However there’s now not numerous subject matter within the outer Milky Manner, so it’s laborious to construct stars sufficiently big to finish their lives in large, element-spewing explosions (SN: 11/2/21). Past 49,000 light-years from the galaxy’s heart, there is just one supernova remnant identified, Ziurys says.
A technique phosphorus will have ended up within the outer galaxy is thru a supernova nearer to the middle that introduced a “galactic fountain,” Ziurys says. “A supernova explodes, the fabric will get thrown out of the galactic airplane, then settles back off close to the galactic edge.” The fabric can be very diluted there, however “if there are other supernovae going off, they’re going to stay polluting the outer galaxy,” she says.
“The detection of the phosphorus-bearing molecules … turns out transparent and compelling,” says Francesco Fontani, an astrophysicist on the Italian Institute for Astrophysics in Florence, who used to be now not concerned within the learn about. He has noticed probably the most different primary components for existence within the outer galaxy, however by no means phosphorus.
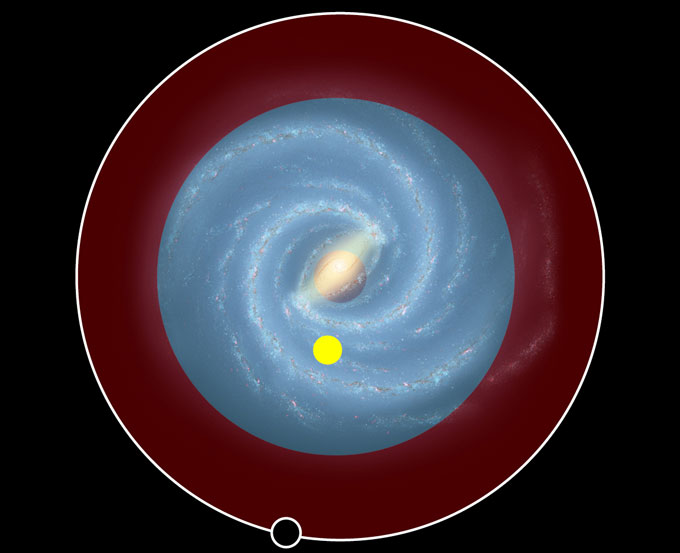
As a result of astronomers had now not discovered the six life-essential components to this point from the galactic heart, they assumed the area the place existence may just exist within the Milky Manner — what’s known as the galactic liveable zone — prolonged at maximum to the farthest supernova they’d discovered, about 52,000 gentle years from the galactic heart. There’s an assumed internal edge as smartly at about 6,500 light-years from the galaxy’s core. The rather massive numbers of supernovas happening there would divulge any planets within the area to intense ultraviolet and X-ray radiation, making it tough for existence to final for lengthy.
“This detection, at the side of earlier detections of natural molecules at an identical massive distances from the galactic heart, helps the concept that the outer barriers of the galactic liveable zone might be wider than what we up to now idea,” Fontani says.
For existence to emerge to this point from the galaxy’s heart, planets would want to exist available in the market. Up to now, they have got been noticed best rather with reference to the sun machine — maximum inside a couple of thousand light-years. “I don’t assume we all know at the moment whether or not they are able to sort at better galactic-central distances,” Ziurys says. Discovering the six components for existence on the galaxy’s edge, she says, will expectantly spur at the seek for probably the most far-off puts the place it would thrive.
