From the Spring 2024 factor of Dwelling Hen mag. Subscribe now.
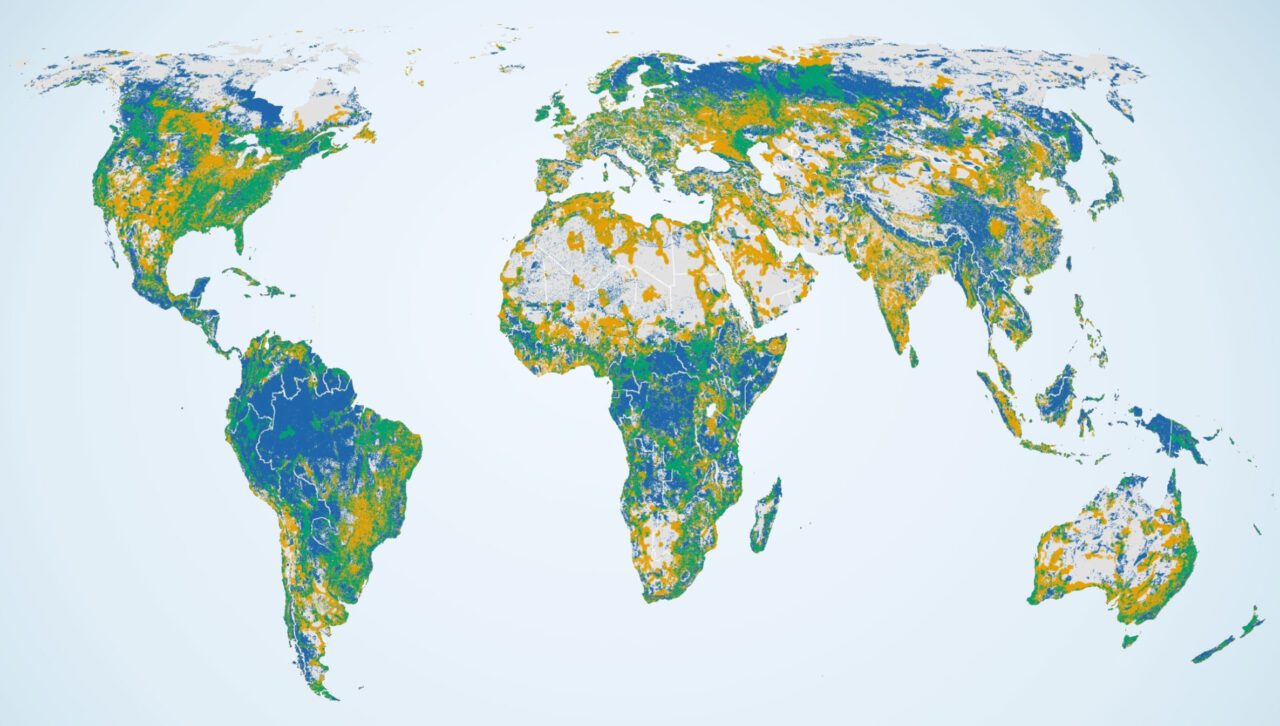
New analysis signifies that strategically safeguarding just below part of Earth’s land may just deal with the majority of nature’s contributions to folks—like water high quality, meals, flood coverage, and carbon garage—whilst additionally assembly the wishes of tens of hundreds of animal species from birds to mammals to reptiles. Alternatively, best 18% of the ones important landscapes are these days secure, and greater than a 3rd of those lands are at prime chance for construction.
Ecologist Rachel Neugarten, lead writer of the analysis printed in January in Nature Communications, says those spaces warrant explicit consideration as the sector scrambles to fulfill biodiversity and local weather exchange goals.
“Biodiversity, local weather, and maintainready construction can’t be thought to be in isolation,” she says. Neugarten, who won her PhD from Cornell University and is now the chief director of conservation making plans on the Natural world Conservation Society, says that conservation and sustainability efforts will have to consider “how a lot nature you want to deal with wholesome fisheries, pollination products and services for agriculture, flood mitigation, coastal coverage, etcetera. The entire issues that folks depend on.”
A key end result of the analysis was once a map appearing spaces—similar to mangroves, forests, grasslands, and shrublands—the place biodiversity, nature’s contributions to folks, and possible long run construction overlap. One space of interphase that stood out in North The usa was once the Southeast, particularly the peaks, valleys, and foothills of the Southern Appalachians.
The Southern Appalachians are identified for freshwater organic diversity, web hosting globally important concentrations of fish, crayfish, mussels, and salamanders. The area could also be house to necessary populations of Golden-winged Warbler, Bachman’s Sparrow, and Prairie Warbler—all 3 indexed as Tipping Level species within the 2022 State of the Birds document. Consistent with the Highland Organic Station, the Southern Appalachians comprise greater than 10,000 documented species of animals, vegetation, and fungi—making it one of the biodiverse temperate areas on the earth.
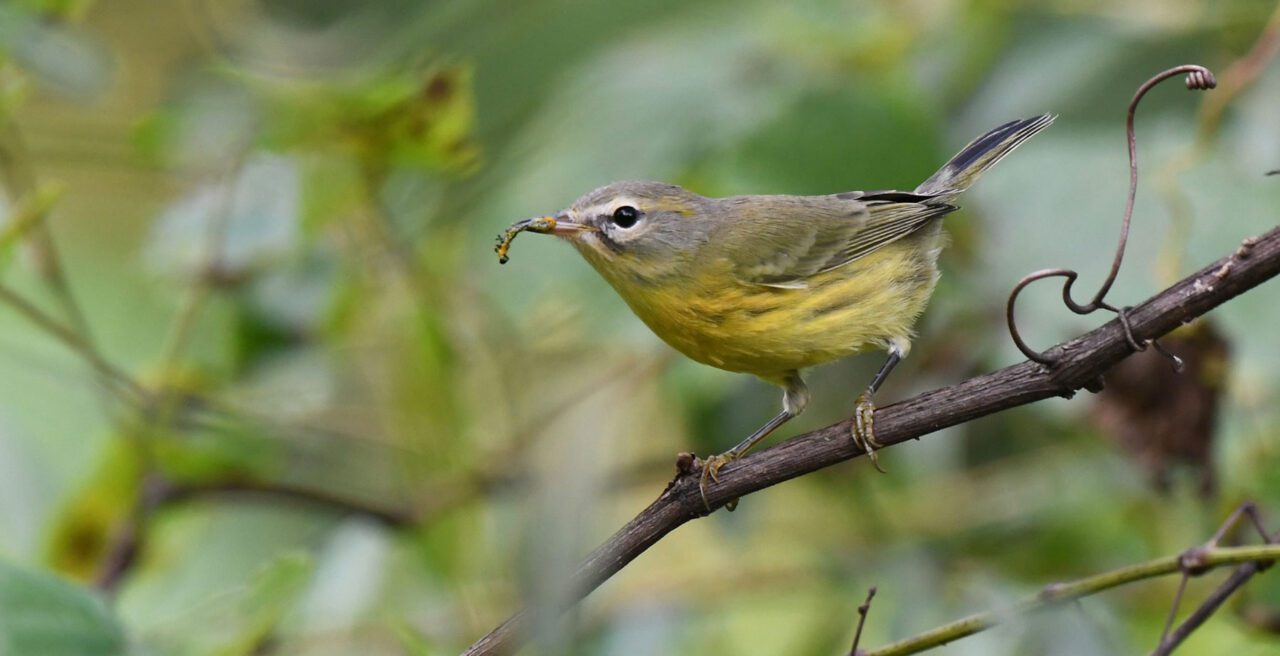

The area additionally delivers necessary ecosystem products and services for folks, says Neugarten: “The entirety from carbon [storage], agriculture, bushes, water high quality, even flood coverage … the forests take in water when there may be an excessive amount of, and unlock it when there may be too little.”
Neugarten and her staff have been surprised to search out that renewable power construction, similar to sun and wind farms, are poised to impact extra land globally by means of construction than some other form of possible use.
“We generally tend to think about agriculture as the most important driving force of habitat conversion and degradation, which is right traditionally, however going ahead it’s more likely to be renewready power,” she says, “since the puts which are extremely appropriate for renewready power haven’t but been transformed.
“Renewable power is basically critical for fighting local weather exchange, but when we’re no longer cautious, that may probably struggle with our conservation objectives.”
Neugarten says cutting edge initiatives are appearing easy methods to maximize advantages in numerous techniques, similar to a sun array in Minnesota the place pollinator habitat beneath sun panels could also be serving to to control stormwater.
Amanda Rodewald, a coauthor of the analysis and senior director of the Cornell Lab of Ornithology’s Heart for Avian Inhabitants Research, says that some of these initiatives display renewable power initiatives can also be in moderation deliberate to deal with nature’s advantages to folks and assist preserve biodiversity.
“With restricted sources to be had to deal with local weather exchange, biodiversity loss, poverty, and water lack of confidence, we will have to be strategic and artistic and in finding techniques to take on a couple of problem at a time,” Rodewald says.
