One thing peculiar is occurring to the Antarctic’s sea ice. The areal expanse of floating ice fringing the continent is not just at a listing low for this time of 12 months — surpassing a listing simply set in 2022 — however ice extent has been hitting listing lows all through the 12 months.
“What’s came about here’s not like the Arctic sea ice expanse,” says Mark Serreze, a local weather scientist and the director of the U.S. Nationwide Snow and Ice Knowledge Middle, or NSIDC, in Boulder, Colo. We’ve come to be expecting a dramatic decline in sea ice at Earth’s different pole, he says (SN: 9/25/19). “No longer a lot has came about to Antarctica’s sea ice till the previous few years. Nevertheless it’s simply plummeted.”
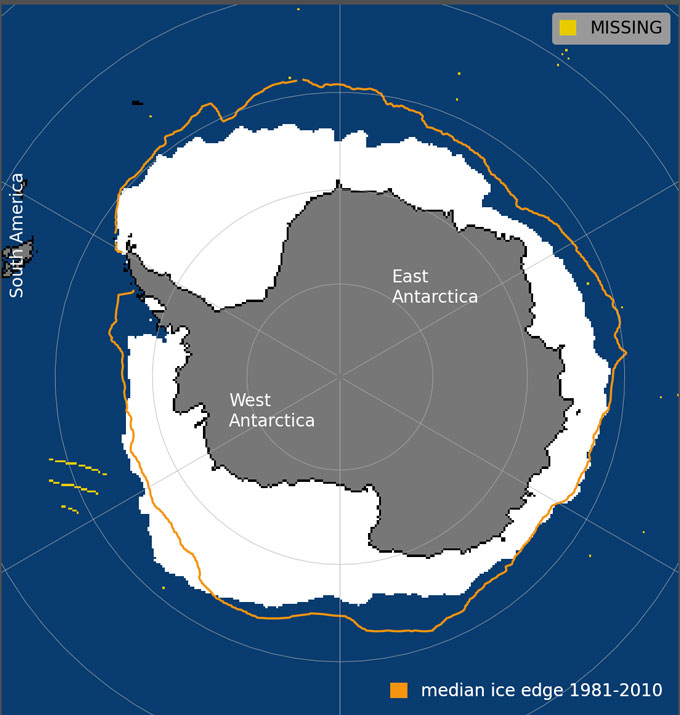
NSIDC makes use of satellite-gleaned information, amassed day by day, to regulate the unfold of sea ice at each poles. All over maximum of 2023, the hoop of sea ice round Antarctica has again and again set new listing lows, staying neatly under the common extent from 1981 to 2010. On February 21 — the peak of the Southern Hemisphere’s summer season — the ocean ice expanse hit an rock bottom since record-keeping started in 1978, of one.79 million sq. kilometers. That’s 130,000 sq. kilometers — concerning the dimension of the state of New York — smaller than the former recorded minimal, reached on February 25, 2022.
Even because the Southern Hemisphere shifted into wintry weather, Antarctic sea ice remained at listing low ranges. On June 27, the ice used to be dotted throughout about 11.7 million sq. kilometers of ocean. That’s about 2.6 million sq. kilometers under the 1981–2010 reasonable, and about 1.2 million sq. kilometers under the former lowest extent on listing for June 27, set in 2022.
In contrast to Arctic ice, whose dwindling is understood to be carefully tied to international warming, it’s been more difficult to parse the explanations for adjustments in Antarctic sea ice extent. That problem has made it unclear whether or not adjustments are the results of herbal variability or whether or not “one thing giant has modified,” Serreze says.
The previous couple of years have given scientists pause (SN: 6/27/17). “We’re more or less shedding off an edge,” Serreze says. It’s now not but transparent whether or not this 12 months’s extent is a part of a bigger development, he notes. However “the longer that persists, the much more likely it’s that one thing giant is occurring.”
The Arctic and the Antarctic areas are polar opposites, so that you can talk, of their geographic atmosphere. Ice within the Arctic Ocean is confined to a fairly small frame of water ringed by means of land. The Antarctic, against this, is a landmass surrounded by means of ocean, this means that the ocean ice across the continent is a lot more cell than up north, with a bigger seasonal vary because it expands within the Southern Hemisphere’s wintry weather and shrinks in summer season. Local weather simulations have, accordingly, constantly predicted that the Arctic would display larger sea ice losses because the planet warms, a minimum of to start with, whilst Antarctica can be slower to reply.
As to why the Antarctic ice has tracked so low this 12 months there are a couple of imaginable culprits. Regional local weather patterns — specifically an air power development referred to as the Southern Annular Mode that shifts the course of winds blowing across the continent — can pack or diffuse the ocean ice quilt round Antarctica. And different regional patterns, such because the El Niño Southern Oscillation, can impact each ocean and air movement within the southern top latitudes.
At the moment, scientists are involved maximum with what lies underneath the ice (SN: 12/13/21). “There’s rising proof that there was some more or less exchange in ocean movement this is bringing extra warmth” to the area, which impacts the ice quilt, Serreze says. “There are a number of other people taking a look into this; we’re in point of fact blitzing to get the information. We wish to perceive what the heck is occurring within the ocean.”
