A flip-flopping, yearslong development of winds is helping keep watch over the destiny of the Arctic’s sea ice — through regulating how a lot of the Atlantic Ocean’s reasonably heat, salty water sneaks northward into the Arctic Ocean.
From 2007 to 2021, winds over North The us and Eurasia have been circulating in this type of means that they decreased the inflow of hotter Atlantic water into the Arctic, researchers document within the Sept. 1 Science. That helped gradual the speed of sea ice loss all through that time frame — at the same time as atmospheric warming ramped up (SN: 8/11/22). However that grace duration might come to an finish inside only some years. When the winds shift again, enhanced “Atlantification” of the Arctic might accelerate sea ice loss, through giving an additional oomph of warming from beneath.
“This segment has lasted about 15 years. We’re about on the finish,” says bodily oceanographer Igor Polyakov of the College of Alaska Fairbanks. “The ocean ice can be responding. There’s a perfect risk for this speedy alternate within the device.”
Earth’s busy, interactive layers of ocean and surroundings function many various regional and international patterns that toggle between two other stages over years to a long time, such because the El Niño and Los angeles Niña stages of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (SN: 6/15/23).
The Arctic Dipole is a smaller-scale, regional development of winds this is having an international have an effect on, Polyakov and associates counsel. To evaluate its affect, the researchers when put next atmospheric wind patterns since 1979 with traits in summer time ice extent and thickness collected from satellite tv for pc, plane and shipboard surveys over that period of time. A transparent dating emerged, they are saying.
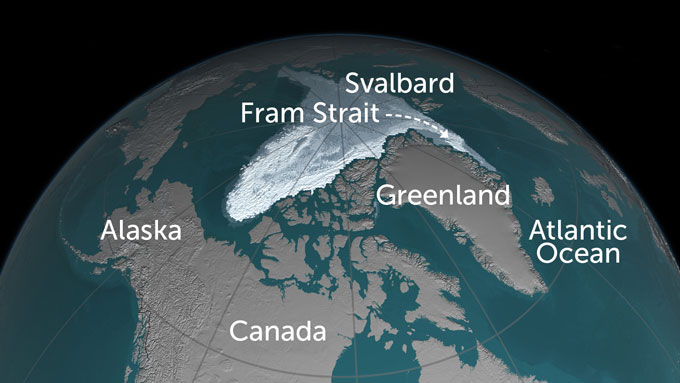
From 1979 to 2006, the Arctic Dipole was once in a “destructive” segment, with winds rotating counterclockwise over North The us and clockwise over Eurasia. That introduced extra Atlantic water into the Arctic by means of the Fram Strait, a slender strip of ocean between Greenland and Norway’s Svalbard archipelago. All through that time frame, summertime sea ice extent shrank abruptly from yr to yr, vanishing at a price of about 1 million sq. kilometers in keeping with decade.
The yr 2007, a record-breaking yr for Arctic sea ice loss, marked the tip of this “destructive” segment of the Arctic Dipole (SN: 12/9/20). From then till 2021, the speed of sea ice loss throughout all of the Arctic slowed, shrinking through best about 70,000 sq. kilometers in keeping with decade — in large part because of atmospheric warming,
That’s to not say that the ice has recovered. It stays at an overly low extent in comparison to the ancient list. Human-caused international warming has ramped up heating around the area and created comments loops that fortify sea ice loss: Melting sea ice exposes extra ocean floor to the solar, warming that floor water, in flip improving ice soften.
However the present, “certain” segment of the Dipole has helped put the brakes at the dramatic price of Arctic sea ice loss — for now, Polyakov says. Much less Atlantic water flowing in throughout the Fram Strait method the waters of the Arctic Ocean stay stratified — tightly layered, with the less-dense, chillier, more energizing Arctic water sitting on peak of the hotter Atlantic waters like a lid on a pot.
That’s been protective the ocean ice from melting from beneath, says Thomas Rippeth, a bodily oceanographer at Bangor College in Wales who was once no longer concerned within the new learn about. Whether or not any other switchover within the Arctic Dipole is ready to happen, moving winds and inspiring extra heat waters to glide northward, isn’t but transparent, Rippeth says. “This paper is telling us what to search for — that’s why it’s a very powerful piece of labor.”
