
From the Spring 2024 factor of Dwelling Chicken mag. Subscribe now.
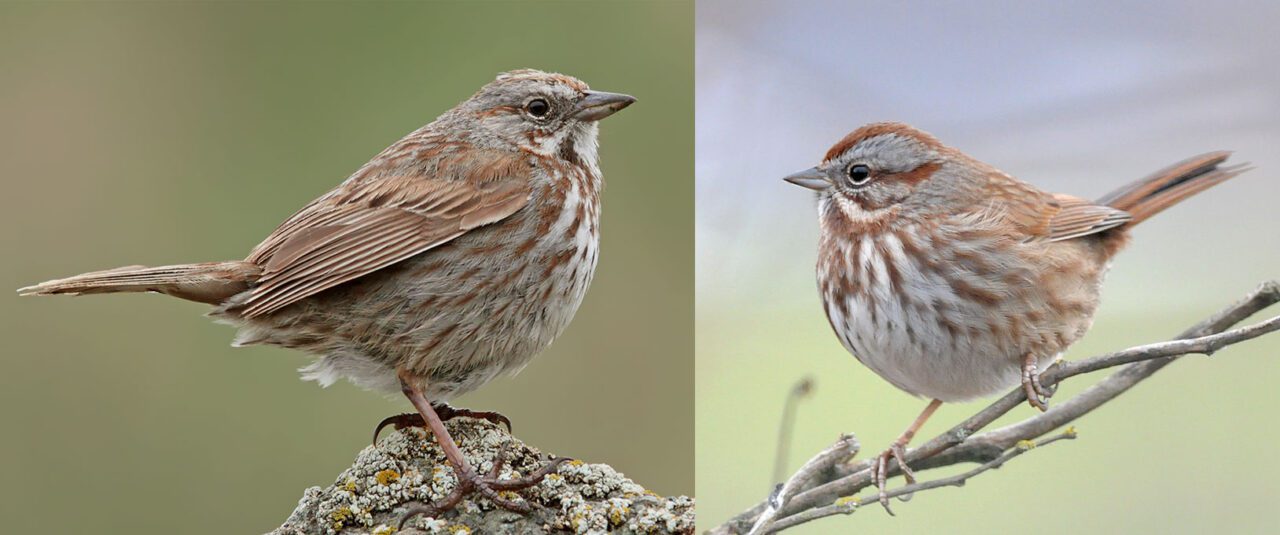
North American Track Sparrows can have some resilience to local weather exchange constructed into their genes, due to a exceptional adaptation that accounts for the beautiful vary of frame sizes discovered all the way through the fowl’s westernmost vary.
That adaptation used to be the point of interest of a find out about, revealed November 7 within the magazine Nature Communications, that provides strengthen for Bergmann’s Rule—a pattern in zoology the place, widely talking, herbal variety in chillier climates ends up in larger-bodied organisms, whilst hotter climates result in smaller our bodies. Amongst organisms that control their very own warmth, bigger our bodies are extra efficient at holding warmth, whilst smaller our bodies permit an organism to stick cooler.
The find out about discovered that Track Sparrows that reside year-round on Alaska’s Aleutian Islands may also be as much as thrice bigger than their cousins close to San Francisco Bay.
“The dimensions distinction amongst Track Sparrows is wild to even consider,” says coauthor Jennifer Walsh, a analysis affiliate on the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. “Our effects display that Track Sparrows have really extensive capability for adapting to native environmental exchange, and the genetic mechanisms underlying the ones adjustments are moderately transparent.”
Walsh and her collaborators conducted whole-genome sequencing and in comparison 79 genomes from 9 Track Sparrow subspecies that happen alongside the Pacific Coast from California the entire approach as much as the outer reaches of Alaska’s islands within the Bering Sea. The genome-sequencing analysis used to be conducted on the Cornell Lab’s Fuller Evolutionary Biology Program.
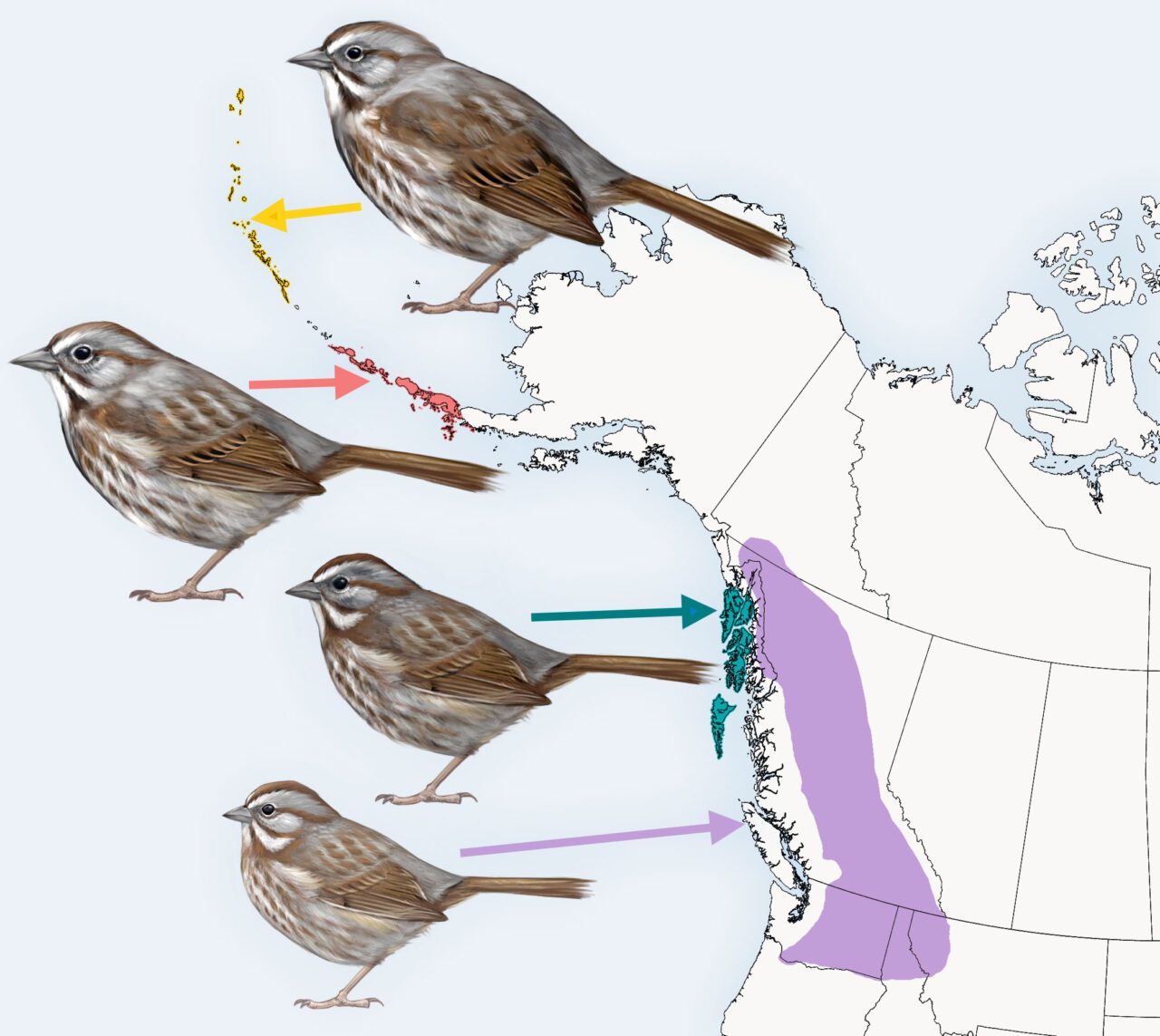
“We discovered 8 gene permutations within the genomes we sequenced, all associated with frame mass as predicted by way of Bergmann’s Rule,” says lead creator Katherine Carbeck, a PhD candidate on the College of British Columbia in Vancouver. “What this tells us is that there’s a genetic foundation for Track Sparrow adaptation to native local weather prerequisites, stretching from the coldest places within the a ways north to the warmest portions of its vary in California.”
Working out the nuances of microevolution makes a distinction on the subject of conservation, the scientists stated. As an example, eBird Developments maps display that Track Sparrow populations in northwestern areas, equivalent to Alaska and British Columbia, are solid or expanding these days, however sparrow populations in California are declining.
Whilst declines in a single portion of the Track Sparrow’s vary may just imply lack of genetic variety in in the community specialised populations, Peter Arcese, a coauthor at the find out about and professor in UBC’s Division of Woodland and Conservation Sciences, says the to findings recommend a resilient long term for those birds—so long as they’ve habitat.
“Our findings indicate that some, if no longer all, in the community tailored Track Sparrow populations might proceed to evolve to local weather exchange, so long as we deal with habitat prerequisites that facilitate the motion of people and genes between populations,” he says.
“Those genomic discoveries display that Track Sparrows had been waxing and waning over millennia. Over that point, every sparrow inhabitants has develop into fantastically fine-tuned to its native atmosphere,” provides Irby Lovette, any other coauthor at the find out about and director of the Fuller Evolutionary Biology Program on the Cornell Lab. “So the legitimate worry is that as environments exchange we would possibly lose the ones tightly matched diversifications.
“But the excellent news is this exact same genetic mosaic creates the uncooked subject material for the sparrows of the longer term to evolve extra temporarily, simply so long as their populations stay wholesome overall such that they are able to transfer round to check their characteristics to converting native conditions.”
This find out about is the primary end result of a bigger Cornell Lab analysis effort to collection Track Sparrow genomes from throughout North The us, spanning just about the entire 25 identified subspecies.
