
Histomoniasis, regularly referred to as blackhead illness, is led to via an anerobic protozoan parasite, Histomonas meleagridis. Histomoniasis impacts all gallinaceous birds and turkeys are essentially the most prone species. Lately, higher incidences of histomoniasis had been documented in chickens.
Vijay Durairaj1, Mary Drozd2, Emily Barber1, Brandon Doss3, Ryan Vander Veen1
1 Huvepharma, Inc., Lincoln, Nebraska, USA
2 College of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska, USA
3 Huvepharma, Inc., Peachtree Town, Georgia, USA
Corresponding creator: [email protected]
A case document of histomoniasis in a four-week-old-broiler breeder pullet farm is mentioned right here. On box investigation, gross lesions in ceca and liver have been spotted suggesting histomoniasis. All through histopathological analysis, Histomonas trophozoites have been known. H. meleagridis and Blastocystis spp. have been remoted in tradition. Complicated molecular diagnostic tactics showed genotype-1 H. meleagridis. With the absence of business vaccines and prophylactic/healing measures, box surveillance research play a very important position in figuring out H. meleagridis wild-type traces and figuring out answers for histomoniasis.
Creation
Histomoniasis was once first reported in turkeys via Cushman (1893). Histomonas meleagridis, an anerobic protozoan parasite, reasons histomoniasis (histomonosis, enterohepatitis, enzootic typhlohepatitis). H. meleagridis impacts all gallinaceous birds and turkeys are extremely vulnerable. Heterakis gallinarum, the typical cecal computer virus of chickens, acts as a vector for transmitting H. meleagridis. Heterakis gallinarum eggs can harbor H. meleagridis for a number of years. Thus, it isn’t really useful to rear chickens and turkeys at the similar premise or in shut proximity to each other.
A number of the gallinaceous species, turkeys are extremely vulnerable to histomoniasis. In turkeys, the mortalities can succeed in as much as 80%-100% (Hess, 2020). Chickens mount a greater immune reaction to H. meleagridis in comparison to turkeys (Powell et al., 2009; Mitra et al., 2017). Thus, the severity of histomoniasis isn’t as pronounced in chickens and would possibly induce mortality as much as 10%-20% (McDougald, 2005). In keeping with 1986 AAAP Committee on Illness Reporting, the commercial losses related to histomoniasis are extra important in chickens in comparison to turkeys because of the selection of birds concerned and frequency of incidences (Callait, 2002). Lately, higher incidences of histomoniasis had been documented in chickens.
Prior to now, histomoniasis was once controlled and regulated via prophylactic remedy with Arsenics (i.e Carbarsone and Nitarsone), and healing remedy with Nitro-imidazoles (Dimetridazole, Iprondidazole) and Nitrofurans (Furazolidone, Salfuride) (Clark, 2017). Because of more than a few causes, those merchandise have been got rid of/withdrawn from the marketplace. At this time, there are not any industrial vaccines to be had to battle histomoniasis. In positive nations, a couple of healing/ prophylactic merchandise are used to battle histomoniasis, however the efficacy of those merchandise are extremely variable.
With this set of instances, the prevention of histomoniasis transmission via following strict biosecurity measures is helping in minimizing the chance of spreading the illness. Box surveillance research support in figuring out the present H. meleagridis wild-type isolates and to identification possible answers for histomoniasis.
Fabrics and strategies
Case historical past
In Spring 2022, histomoniasis was once reported in two out of 7 properties (n=14,000 birds/space) in four-week-old-broiler breeder pullets in South Central, USA. Greater mortality was once reported in each properties. On necropsy, gross lesions have been spotted within the ceca and liver. Ceca and liver samples have been gathered in 10% impartial buffered formalin for histopathological analysis. Further cecal samples have been gathered in plug seal-capped flasks containing 10 ml of changed Dwyer’s media (Hauck, 2010) and positioned in a heat insulated Styrofoam field and safely transported to the lab. As well as, entire intestines have been gathered and shipped in a chilly insulated Styrofoam field.
Histopathology
Necropsy tissues have been in an instant mounted in 10% impartial buffered formalin. Following fixation, sections have been processed robotically, paraffin-embedded and sectioned at 3-4 μm and stained with hematoxylin-eosin. Histologic tissues have been evaluated via a board-certified pathologist.
Tradition
The plug seal-capped flasks with cecal samples have been won in heat situation. The flasks have been supplemented with contemporary pre-warmed changed Dwyer’s media (5 ml) after which moved to an incubator (40°C) and maintained in anaerobic situation. Periodically, the cultures have been seen below inverted microscope.
DNA extraction and PCR
Intestinal samples have been evaluated and a work of cecal tissue was once homogenized with glass beads. DNA was once extracted from the homogenized cecal pattern the use of DNeasy Blood & Tissue Equipment (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the producer’s directions. Each and every 50 µL PCR response consisted of 1X GoTaq G2 Sizzling Get started Inexperienced Grasp Combine (Promega, Madison, WI), 0.2 µM of every primer, and 5 µL of template. PCR was once carried out the use of protozoa 18s rRNA primers (9. Bilic 2014), H. meleagridis rpb1 gene explicit primers (9. Bilic 2014), SSU rRNA of Blastocystis primers (10. Hess et al., 2006), and mtCOI gene of Eimeria sp. primers at the side of the described biking stipulations.
Gel electrophoresis of PCR merchandise and sequencing
The amplicons (2 µL) have been visualized the use of E-Gel™ EX Agarose Gels, 2% (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) with E-Gel™ 1 Kb Plus DNA Ladder (Invitrogen™). The QIAquick PCR purification package (Qiagen) was once used to purify the PCR merchandise for sequencing (Eurofins, Louisville, KY).
Effects
Gross pathology
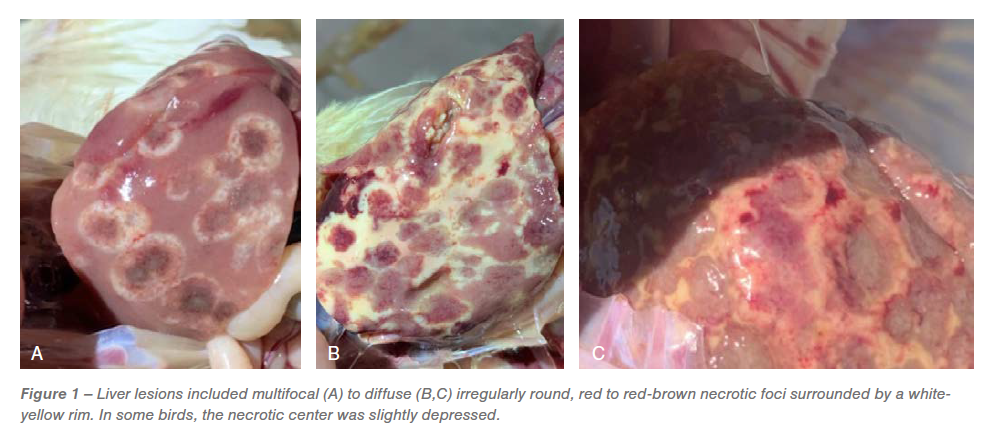
Gross lesions within the ceca incorporated typhlitis and cecal cores. The liver lesions had a lot of darkish pink focused multifocal necrotic foci surrounded via white outer edge comparable to bulls-eye (Determine 1A), diffuse irregularly spherical, pink necrotic foci surrounded via white-yellow rim, leading to discoloration of the liver (Determine 1B) and red-brown necrotic foci leading to slight depressions at the floor of the liver comparable to saucer formed lesions (Determine 1C). In keeping with the unique gross lesions within the ceca and liver, a presumptive prognosis of histomoniasis was once made.
 Histopathology
Histopathology
Ceca: Roughly 60% to 95% of the mucosa was once changed via predominately granulomatous irritation and granulation tissue infiltrated via pleomorphic micro organism and Histomonas trophozoites (Figures 2 and three). The luminal floor was once coated in a fibrinocellular exudate infiltrated via protozoa and micro organism. The underlying submucosa was once effaced via histiocytic to pyogranulomatous irritation and granulation tissue this is infiltrated via trophozoites (Figures 2 and three). 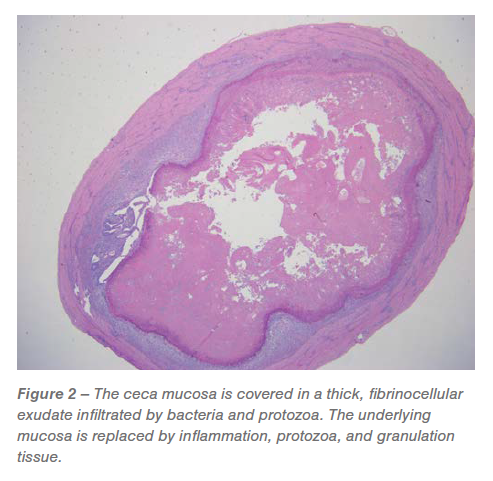
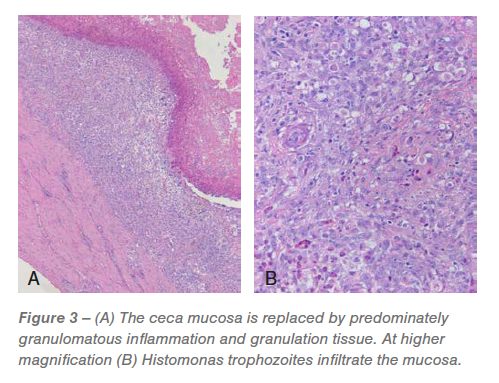
The remainder mucosa had plentiful lamina propria fusion and irritation, bacterial and protozoa, crypt loss and in depth, abnormal distention of the rest crypts with protein and mobile particles. The tunica muscularis was once expanded and mildly effaced via multifocal to coalescing, predominantly histiocytic irritation this is maximum prevalent round small blood vessels and from time to time has a central nidus of necrosis and trophozoites. The related mesentery was once thickened via lymphohistiocytic irritation.
Liver: Between 20% and 75% of the tested liver sections have been seriously effaced via multifocal to coalescing, random, hepatocellular necrosis infiltrated via histiocytic and combined irritation with granuloma group, variable numbers of trophozoites and protein (Determine 4). 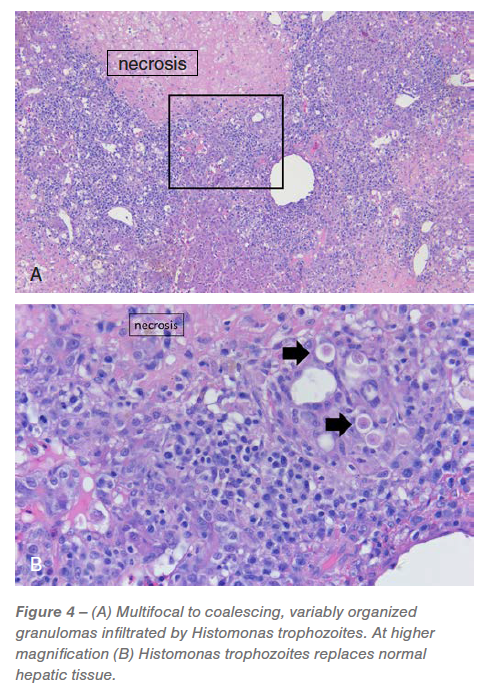
Tradition
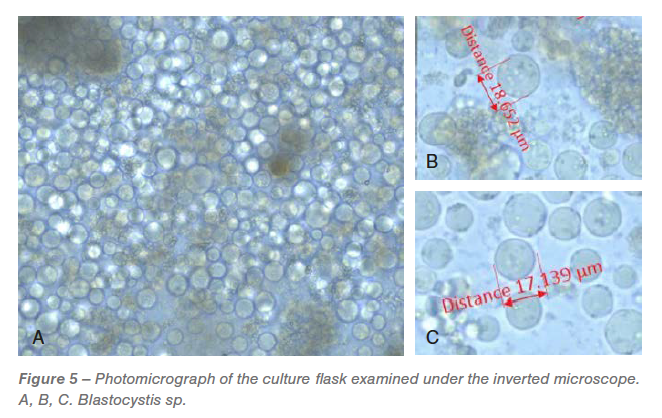
At the day after receipt, all of the flasks have been tested below the microscope. An crushed Blastocystis spp. inhabitants (Determine 5) with various sizes have been seen in all of the flasks. Two days after incubation, H. meleagridis have been detected within the tradition however have been tricky to report via microscopic pictures because of overwhelming expansion of Blastocystis spp. The entire flasks had unidentified bacterial inhabitants.
 PCR and sequencing
PCR and sequencing
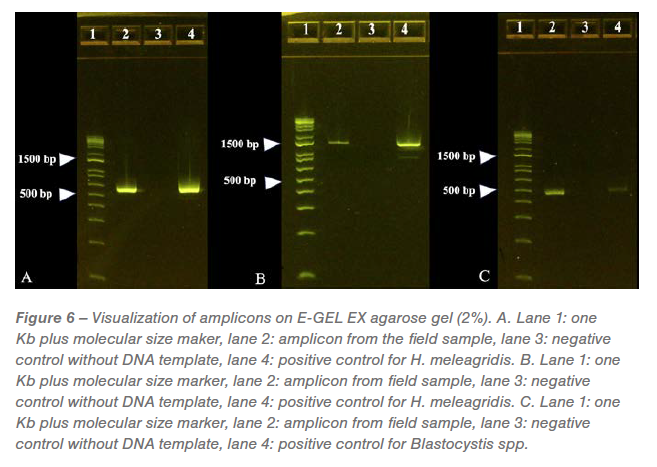
The expected measurement of every amplicon generated from the PCR reactions was once visualized on separate E-Gels. A favorable band was once spotted at roughly 550 bp within the amplicons generated via PCR directed in opposition to protozoal 18s RNA and showed as genotype-1 H. meleagridis with 95.17% identification to wild-type H. meleagridis (Determine 6A). A favorable band was once spotted at roughly 1240 bp within the amplicons generated via PCR directed in opposition to H. meleagridis Rpb1 gene and showed as genotype-1 H. meleagridis with 99.66% identification to wild-type H. meleagridis (Determine 6B). A favorable band was once spotted at roughly 500 bp within the amplicons generated via PCR directed in opposition to Blastocystis spp. with 99.30% identification to wild-type Blastocystis spp. (Determine 6C). No bands have been seen on Eimeria sp. explicit PCR (gel symbol no longer proven).
 Dialogue
Dialogue
Histomoniasis in chickens was once now and again reported prior to now. Withdrawal and ban of prophylactics/therapeutics in poultry has led to higher circumstances of histomoniasis. The selection of birds concerned, at the side of higher incidences and accompanying morbidity and mortality, has situated histomoniasis as an economically vital illness within the hen business. In america, a day-old broiler breeder feminine chick prices ~ $10 and male chick prices ~$14. Bearing in mind the feeding, control and hard work prices at four-weeks-of-age, a broiler breeder pullet prices roughly $13 to $17. As an example, in a flock of 14,000 birds at four-weeks-of-age, if 1% of higher mortality is on account of histomoniasis, it’ll lead to further losses of $1820-$2380. If the mortality related to histomoniasis higher to five%, it’ll lead to an extra lack of $9,100 to $11,900.
A presumptive prognosis of histomoniasis was once made in accordance with the function gross lesions within the ceca and liver. On this case, the liver lesions have been unique suggesting histomoniasis. In some circumstances, H. meleagridis does no longer motive conventional lesions within the liver. In different circumstances, the liver and cecal lesions could also be caused via other pathogens. Lesions within the hen liver can also be caused via parasites comparable to H. meleagridis, Tetratrichomonas gallinarum and Leucocytozoon caulleryi, viruses comparable to Marek’s illness virus, Avian leukosis virus, reticuloendothelial virus, bird adenovirus-1, avian hepatitis E virus and micro organism comparable to Salmonella pullorum, Salmonella gallinarum, Pasteurella multocida, Mycobacterium avian, Enterococcus cecorum, Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus, Escherichia coli (perihepatitis), Mycoplasma gallisepticum (perihepatitis), Mycoplasma synoviae (perihepatitis), Clostridium perfringens, Camplylobacter hepaticus, Staphylococcus, and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Different stipulations that may motive liver lesions come with hemorrhagic hepatopathy, fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome, aflatoxins, amyloidosis, ascites, visceral gout, warmth tension and prime power vitamin. Lesions within the hen ceca can also be caused via parasites comparable to H. meleagridis, Eimeria tenella, Tetratrichomonas gallinarum and micro organism comparable to Salmonella sp. Mixed liver and cecal lesions in chickens can also be caused via H. meleagridis, Tetratrichomonas gallinarum and Salmonella Sp.
Histology of the ceca and liver showed H. meleagridis as the reason for necroulcerative typhilitis and necrotizing and granulomatous hepatitis in those chickens.
The cecal tradition incubated in changed Dwyer’s media had overwhelming expansion of Blastocystis spp. of more than a few sizes. Blastocystis spp. is a commonplace protozoan parasite this is provide within the gut of the chickens (Grabensteiner et al., 2006; Chadwick et al., 2000). Even supposing arguable, Blastocystis sp. does no longer have an enormous medical affect (Chadwick et al., 2000; Stensvold et al., 2009).
H. meleagridis has two genotypes, specifically genotype 1 and a pair of (Bilic et al., 2014). The pathological manifestations and the medical indicators range between the genotypes. PCR and sequencing showed that the wild-type H. meleagridis reported on this learn about was once genotype 1. In Europe, genotype 1 is primary, whilst genotype 2 is uncommon (Bilic et al., 2014). In america, in accordance with our box surveillance over the previous few years, genotype 1 was once known in all of the box outbreaks studied. Complicated molecular tactics comparable to PCR and sequencing is helping supply precious insights on the genotype degree. Thus, box surveillance research assist in figuring out present H. meleagridis wild-type isolates and can also be helpful in figuring out an answer for histomoniasis.
Acknowledgment
The authors want to thank the poultry corporate and the manager for participating on this box case.
References
- Cushman, S. The manufacturing of turkeys. In: Bulletin 25, Agricultural Experiment Station, Rhode Island School of Agriculture and Mechanical Arts, Kingston, RI. 89–123. 1893.
- Hess M., McDougald LR. Histomoniasis. In: Swayne D, Boulianne M, Logue C, McDougald L, Nair V., Suarez D., deWit S., Grimes T., Johnson D., Kromm M., et al., editors. Sicknesses of Poultry. 14th ed. Ames (IA): Wiley- Blackwell. 1223–1230; 2020.
- Powell, F. L., L. Rothwell, M. J. Clarkson, and P. Kaiser. The turkey, in comparison to the hen, fails to mount an efficient early immune reaction to Histomonas meleagridis within the intestine. Parasite Immunol. 31:312–327. 2009.
- Mitra, T., W. Gerner, F. A. Kidane, P. Wernsdorf, M. Hess, A. Saalmuller, and D. Liebhart. Vaccination in opposition to histomonosis limits pronounced adjustments of B cells and T-cell subsets in turkeys and chickens. Vaccine 35:4184–4196. 2017.
- McDougald LR. Blackhead illness (histomoniasis) in poultry: a important overview. Avian Dis. 49:462–476; 2005.
- Callait, M. P., C. Granier, C. Chauve, and L. Zenner. In vitro job of healing medication in opposition to Histomonas meleagridis (Smith, 1895). Poult. Sci. 81:1122–1127. 2002.
- Clark S, Kimminau E. Important overview: long run regulate of blackhead illness (histomoniasis) in poultry. Avian Dis. 61:281–288; 2017.
- Hauck R, Armstrong PL, McDougald LR. Histomonas meleagridis (Protozoa: Trichomonadidae): research of expansion necessities in vitro. J Parasitol. 96:1–7; 2010.
- Bilic I, Jaskulska B, Souillard R, Liebhart D, Hess M. Multi-locus typing of Histomonas meleagridis isolates demonstrates the life of 2 other genotypes. PLOS ONE 9:e92438; 2014.
- Hess, M., T. Kolbe, E. Grabensteiner, and H. Prosl. Clonal cultures of Histomonas meleagridis, Tetratrichomonas gallinarum and a Blastocystis sp. established thru micromanipulation. Parasitology. 133:547–54. 2006.
- Grabensteiner, E., and M. Hess. PCR for the id and differentiation of Histomonas meleagridis, Tetratrichomonas gallinarum and Blastocystis spp. Vet. Parasitol. 142:223–230. 2006.
- Chadwick E, Malheiros R, Oviedo E, Cordova Noboa HA, Quintana Ospina GA, Alfaro Wisaquillo MC, Sigmon C, Beckstead R. Early an infection with Histomonas meleagridis has restricted results on broiler breeder hens’ expansion and egg manufacturing and high quality. Poult Sci. 99:4242-4248. 2020.
- Stensvold CR, Alfellani MA, Nørskov-Lauritsen S, Prip Ok, Victory EL, Maddox C, Nielsen HV, Clark CG. Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolates from synanthropic and zoo animals and id of a brand new subtype. Int J Parasitol. 39:473-9. 2009.
