Some newly reported clumps of cells rising in lab dishes were hailed as the nearest issues to human embryos that scientists have ever made within the lab.
Those entities are human embryo fashions — plenty of cells produced from stem cells that mimic some homes of positive phases of embryo building. The success offers researchers an opportunity to have a look at human building past the primary week or so, when an embryo will have to implant within the uterus to increase additional. That post-implantation level hadn’t been re-created in lab dishes — till now.
Six research reported in June and July describe the embryo fashions, that have generated pleasure and fear in equivalent measure.
For researchers running on those embryo fashions, the pretend embryos are new equipment to realize perception into the “black field” of human building, after embryos implant within the uterus. They’re helpful as a result of donated human embryos are briefly provide, and there are limits at the kinds of experiments researchers can carry out on them.
About 60 p.c of pregnancies fail simply ahead of, all the way through or quickly after implantation, developmental and stem mobile biologist Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz of the College of Cambridge and Caltech mentioned June 27 all the way through a information briefing discussing an embryo type made in her lab. Insights gleaned from the embryo fashions can give new figuring out of why many pregnancies fail to take grasp and result in higher fertility remedies, Żernicka-Goetz mentioned.
However others concern that the fashions — along side eggs and sperm made out of stem cells — lift the threat of researchers the usage of the mimics to create small children. Scientists creating the fashions say replica isn’t their intention or aim, and that implantation in a uterus is inconceivable with those embryo fashions.
Nonetheless, the analysis raises problems with the way to — and whether or not to — keep watch over what scientists can do with embryo-like entities made out of stem cells. Questions encompass whether or not embryo fashions may just or will have to be grown previous the identical of 14 days of ordinary human building after fertilization. And critics warn that overstating what the fashions are or can do may just dangers harmful accept as true with in science.
Science Information talked to scientists and ethicists to be told extra about those human embryo fashions.
What are human embryo fashions?
Sooner than answering that query, Amander Clark, president of the Global Society for Stem Cellular Analysis, says we first wish to take into account that a human embryo is the made of fertilization of an egg and sperm.
Embryo fashions, however, self-assemble from pluripotent stem cells — ones that experience the ability to make just about any form of mobile within the physique. “Subsequently, embryo fashions don’t meet the medical, clinical or clinical definition of an embryo as a result of they don’t originate from the made of fertilization by means of two gametes,” says Clark, a stem mobile scientist, developmental biologist and geneticist at UCLA.
For years, scientists have studied the primary week or so of human building the usage of donated human embryos or embryo fashions (SN: 1/5/22). From the ones, researchers discovered an ideal deal concerning the formation of the ball of cells referred to as a blastocyst. Blastocysts have an outer layer of cells that can sort the placenta and different strengthen methods for the creating embryo, and an inside cluster of cells that can give upward thrust to the physique.
But it surely’s the following few weeks of existence when the actual motion occurs, says stem mobile biologist and embryologist Jacob Hanna of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel. Between day seven and about day 35 after fertilization is when the embryo builds all its organs. “It strikes from a ball of cells to a construction that anyone in the street … would inform you, ‘That is an embryo.’ After which the remainder of the opposite 8 months are simply enlargement of the embryo,” he says.
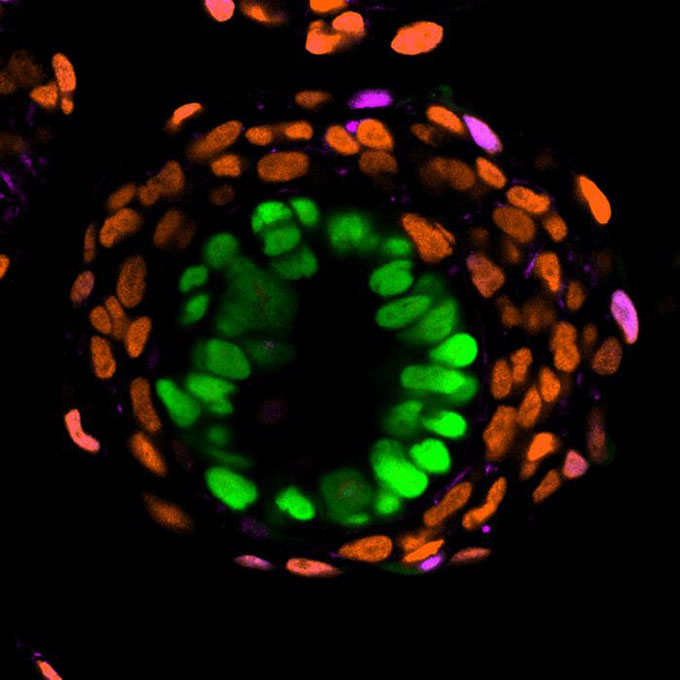
Researchers have assembled embryo fashions that comprise some, however no longer all, of the kinds of cells essential for standard building. The newly reported embryo fashions mimic constructions that will be present in an embryo that has implanted in a uterus, even if the mimics don’t have anything to implant into. The fashions are simulating an overly explicit window of embryo building: “the occasions that happen as an embryo implants, how the embryo self-assembles,” Clark says. “Then necessarily they cave in.”
Not one of the fashions utterly replica an actual embryo, she says. As an example, none make an excellent trophectoderm, the layer of cells that provides upward thrust to the placenta later in building. That layer is necessary for an embryo to implant into the uterus, and it additionally sends indicators that lend a hand the remainder of the embryo increase correctly.
How did the most recent buzz about embryo fashions get started?
Put up-implantation embryo fashions drew media consideration when Żernicka-Goetz introduced initial findings within the final moments of a chat she gave June 13 in Boston at a gathering of the Global Society for Stem Cellular Analysis. The Dad or mum newspaper hailed the paintings as a step forward that created artificial human embryos.
That characterization overstates the success, says Alfonso Martinez Arias, a developmental biologist at Pompeu Fabra College in Barcelona. The paintings isn’t a step forward, however an incremental advance, and is a ways from re-creating an embryo, he says.
Żernicka-Goetz and associates genetically engineered human stem cells to resemble 3 kinds of cells essential for embryo building: cells that mimic the necessary placenta-generating trophectoderm, cells that resemble ones that can sort the yolk sac that feeds the embryo till the placenta takes over, and ones that sort the epiblast — the cells throughout the embryo that can transform the physique. The ensuing balls of cells resemble some sides of human embryos, the crew reported June 27 in Nature.
As an example, the trophectoderm layer bureaucracy at the out of doors of the embryo-like construction because it does in embryos. But it surely doesn’t make proteins conventional for that layer when assembled in a 3D construction, so it isn’t in reality a placental precursor, coauthor Bailey Weatherbee of the College of Cambridge mentioned all the way through the scoop briefing. However the layer is essential for the remainder of the embryo type to collect, suggesting it plays one of the most purposes of the trophectoderm, she mentioned.
How have been different embryo fashions made?
Like Żernicka-Goetz’s crew, all of the analysis teams began with human stem cells. In moderation controlling rising stipulations and the numbers of positive kinds of cells added to the combo allowed the stem cells to develop into embryo-like constructions. The fashions vary within the collection of mobile sorts they comprise and within the options of actual embryos they’re in a position to imitate.
One staff of researchers coaxed stem cells to sort embryo-like constructions with two tissue layers. That paintings, additionally described June 27 in Nature, didn’t use genetic manipulation or chemical compounds to urge the stem cells to sort embryo-like constructions. As an alternative, the researchers trusted stem cells’ talent to self-organize, says developmental biologist Berna Sozen of Yale Faculty of Drugs.
The ensuing type lacks the trophectoderm. When the researchers learned the tissue was once lacking, they idea its absence may inform them one thing about its significance, she says. “Within the absence of those tissues you’ll see what’s going to occur, what doesn’t occur, and then you definately [get] very robust clinical insights [about] why you wish to have that tissue.”
Every other effort by means of researchers in China and Michigan, described in a not-yet-peer reviewed preprint posted June 16 on-line at bioRxiv.org, is technically spectacular, Martinez Arias says. But it surely nonetheless lacks a placenta precursor layer.
Maximum just lately, a crew led by means of Jun Wu of the UT Southwestern Clinical Heart in Dallas persuaded stem cells to sort embryo-like entities that span the rearrangement tournament known as gastrulation, the researchers file July 20 in Cellular. Right through gastrulation embryos move from hole spheres of cells to multilayered constructions that can give upward thrust to organs and tissues that sort the physique.
Those “peri-gastruloid” fashions made some tissues such as the ones within the early fearful device and would possibly lend a hand ascertain the origins of cells that can give upward thrust to eggs and sperm. Those fashions additionally comprise a yolk sac, however “our type isn’t an entire type,” Wu says. “We don’t have the placenta tissue.”
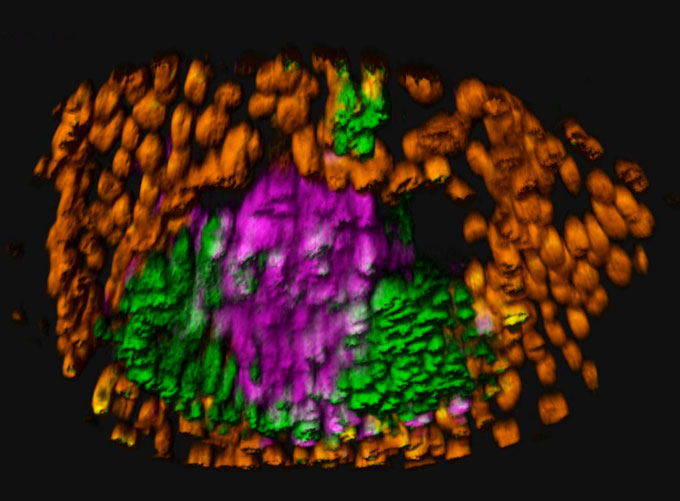
For the reason that fashions lack the trophectoderm, the researchers had so as to add proteins to anchor and strengthen the gastruloids so they might increase correctly.
A crew of researchers in China reported initial result of an identical gastruloids with yolk sacs June 28 at bioRxiv.org. That crew discovered that the chemical thalidomide alters formation of the tissue layers and interrupts building.
One day, researchers may use such fashions to know the way chemical compounds from the surroundings may just have an effect on creating embryos, Wu says.
Martinez Arias and others have up to now made gastruloids that would type building as much as day 19 after fertilization, however the ones previous fashions didn’t have yolk sacs.
Are any of the embryo fashions main advances?
Of this “gold rush” of embryo fashions, handiest two are actual advances, Martinez Arias says: Wu’s gastruloids and embryo fashions made by means of Hanna’s staff.
Hanna’s fashions described in a June 15 preprint posted at bioRxiv.org, have an affordable facsimile of each a yolk sac and the placenta precursor, Martinez Arias says, and make constructions with “uncanny” resemblance to these of embryos at 14 days of building.
The method to reach an embryo type so intently such as the actual factor was once an extended one, Hanna says. His crew first labored out the way to develop mouse embryos previous this developmental level in lab dishes. The usage of mouse embryos as their “experimental compass,” the researchers then discovered the way to construct a mouse embryo type from stem cells. From there, the crew used the tips they’d discovered to develop human stem cells in stipulations that coaxed them to self-assemble into constructions approximating post-implantation embryos.
The self-assembly bypassed the blastocyst level and moved immediately to one thing corresponding to a post-implantation embryo, his crew discovered. “Possibly the embryo [models] are poor as a result of we don’t move to in the course of the blastocyst [stage]. I don’t assume so. However I will’t exclude it these days,” Hanna says.
Can those embryo fashions lead to small children?
No, however that query at all times comes up.
Scientists are desirous about technical and organic advances the brand new embryo fashions convey. However for most of the people, “it’s actually the likelihood that they may well be used for replica that that pulls the eye,” says Katie Hasson, affiliate director of the Heart for Genetics and Society, a nonprofit social justice group based totally in Berkeley, Calif.
It’s no longer imaginable to make use of those embryo fashions for replica, scientists say. “Now not handiest is it unlawful to position those past due level [embryo models] throughout the uterus, however in reality if I sought after to, or any person sought after to, those constructions can by no means implant,” Hanna says. Implantation occurs handiest when embryos consist of 1 to 64 cells. Those post-implantation fashions have moved past that level. Biologically, he says, “it’s going to by no means be triumphant.”
Wu is of the same opinion. “Those fashions aren’t human embryos in any respect,” he says. “They aren’t in a position to generate any form of existence. They’re necessarily only a cluster of cells.”
There are prison blocks to rising embryos within the lab previous a undeniable level as neatly. In the UK, the regulation forbids rising embryos previous 14 days of building, the purpose at which the embryo activates its body-building program. That prohibit was once imposed in a while after in vitro fertilization changed into imaginable.
However a few of these embryo fashions already resemble embryos on the 14-day level of building. Because the fashions aren’t created thru fertilization and may just by no means give upward thrust to an individual, some researchers argue that they shouldn’t be matter to the 14-day rule.
In the USA, there is not any regulation banning rising embryos previous 14 days, however the 1995 Dickey-Wicker modification prohibits the U.S. Nationwide Institutes of Well being from investment analysis on embryos or embryo-like cells with “organismal doable,” Clark says. Since those fashions lack crucial portions, they’ve no doable to make an organism — so analysis with embryo fashions may also be funded.
The world stem mobile society just lately up to date its pointers, suggesting that if scientists need to tradition embryos created by means of fertilization for longer than 14 days, they wish to search public approval of their jurisdiction. Because the fashions aren’t embryos, the society’s pointers counsel that they are able to be cultured up till a construction known as the primitive streak seems, signaling that the embryo is beginning to construct the physique.
The purpose for many scientists within the box is to grasp the method wherein cells construct an embryo after which create all of the organs and tissues of the physique, Martinez Arias says. It’s neither essential nor fascinating, and possibly no longer even imaginable, to construct a great copy of an embryo. “I undoubtedly don’t assume that this is one thing that we need to do, or that we will have to do or will have to say,” he says. “And that’s no longer one thing this is at the horizon.”
Even so, scientists wish to hit the pause button to entirely assessment the embryo-like constructions and decide how they are able to support in figuring out human building, Martinez Arias says. “I’m hoping that now we will all increase those methods in a way that turns out to be useful for analysis, slightly than seeking to see how a ways into area we [can] move, with out considering [about] how we go back.”
Conversations with the general public about what the embryo fashions constitute scientifically, philosophically and legally, and about the way to use them ethically wish to get started now, Hasson says. “We wish to consider them now as it’s no longer the case, and it shouldn’t be the case, that the technical limits of what scientists can lately do with those fashions will have to outline the moral dialogue and what the moral limits will have to be.”
