The dynamic complexity of the growing embryo calls for the upkeep of differentiated compartments with the capability to handle impartial environments required to optimise their serve as. One of the vital least understood homeostatic mechanisms in embryonic construction pertains to the pH.
The albumen’s pH at lay reports a pointy building up to 9.7 which later decreases to six.90 via day 17 (Tona et al., 2001). By contrast, the pH of yolk begins with a reasonably low 6.67 at lay and will increase with the embryonic construction as much as 8.05 at 15 d (Decuypere et al., 2001). This experiment geared toward trying out the speculation that the in ovo injection of oregano very important oil (OEO) at a buffered impartial pH between 6.5 and seven.0 has the prospective to give a boost to the hatchability and the post-hatch efficiency in broiler chickens.
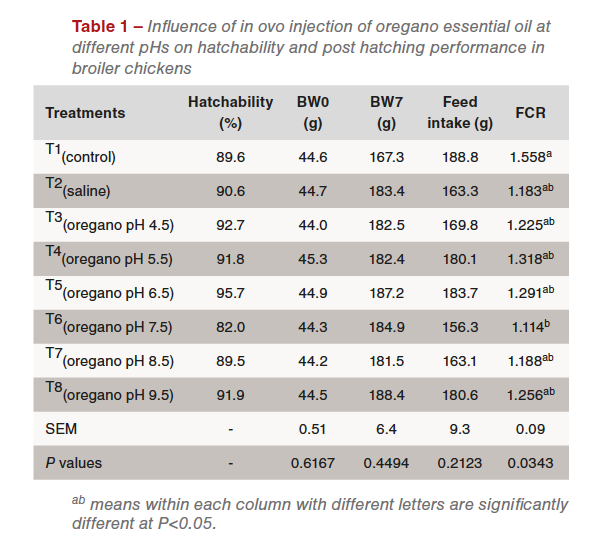
The learn about incorporated 720 eggs incubated the usage of usual procedures. T1-T2 have been keep an eye on teams consisting of three replicates of 20 eggs every non-injected (T1) or injected with a saline resolution (T2) within the air-sac on day 17.5. T3-T8 consisted of five replicates of 20 eggs every injected 0.1ml OEO at other pH, in air sac on day 17.5. The focus of OEO was once 0.5%. The pH resolution for T3 (pH=4.5) was once adjusted the usage of 0.1 mM citric acid, whilst for T4-T8 (pH of five.5, 6.5, 7.5 and eight.5, respectively) 0.001M sodium hydroxide was once used. At 21 d, 45 chicks from teams T1-T8 (3 replicates of 15 chicks/workforce) have been transferred to brooders and reared for 7 days. Knowledge was once analysed the usage of PROC GLM of SAS 9.4. Importance degree was once set at P<0.05.
The easiest hatchability was once seen for the 6.5 pH in T5 (95.7%) whilst T6 (pH 7.5) had the bottom (82.0%) (Desk 1). Injection of OEO with other pH into the air mobile had no vital affect on post-hatch expansion or feed consumption (P>0.05). On the other hand, injection of OEO at a pH of seven.5, in comparison to the non-injected keep an eye on workforce, considerably (P<0.05) lowered feed conversion ratio (FCR) (1.114 vs 1.558). Growth in FCR may well be associated with certain affect of OEO on chickens’ well being, in order that they successfully applied the feed. In conclusion, adjustments within the pH of OEO injected in ovo might affect hatchability and FCR post-hatch in broiler chickens.
Acknowledgements: Learn about was once supported via AgriFutures Hen Meat Program.
References
Decuypere E, Tona Ok, Bruggeman V & Bamelis F (2001) International’s Poult. Sci. J. 57: 127-138.
Tona Ok, Bamelis F, De Ketelaere B, Bruggeman V, Moraes VM, Buyse J & Decuypere E (2003) Poult. Sci. 82: 736-741.