When Brant Robertson noticed a brand new size of the gap to a well-recognized galaxy, he laughed out loud.
For greater than a decade, the galaxy were a contender for essentially the most far-off ever noticed. In 2012, Robertson and co-workers used information from the Hubble House Telescope to turn that the galaxy’s gentle had shone around the universe from about 13.3 billion years in the past — lower than 400 million years into the universe’s life.
Now not everybody believed it. “We were given numerous flak,” remembers Robertson, an astrophysicist on the College of California, Santa Cruz. “It gave the impression too improbable that it used to be at the sort of good distance.” It felt like he used to be going round claiming to have noticed the Loch Ness monster.
However in September, the James Webb House Telescope, JWST for brief, aimed its huge replicate and delicate spectrograph on the similar galaxy and confirmed that Robertson and his colleagues had been proper. The galaxy’s gentle is certainly extremely previous, courting to simply 390 million years after the Giant Bang. It used to be like somebody had tired the lake, and the monster used to be sitting there on the backside.
And this galactic Nessie isn’t on my own. To this point, in its first 12 months of observations, JWST has became up hundreds of far-off galaxies courting to the early universe, many greater than astronomers had anticipated. A few of the ones galaxies are brighter, extra huge or extra mature than astronomers would have concept. They’re now scratching their heads attempting to provide an explanation for how the galaxies will have grown up so rapid.
Numerous the extraordinary distances nonetheless wish to be showed, however preliminary proof suggests there’s reason why to consider that many, if now not maximum, of the galaxies actually are that some distance away.
“I used to be anticipating to seek out some galaxies at this [distance]. Some folks had been pessimistic; I wasn’t,” says Steven Finkelstein, an astrophysicist on the College of Texas at Austin. “However I used to be now not this positive. I assumed, ‘Yeah, yeah, we all know what we’re going to look.’ And I used to be improper.”
The Hubble House Telescope’s far-off galaxies
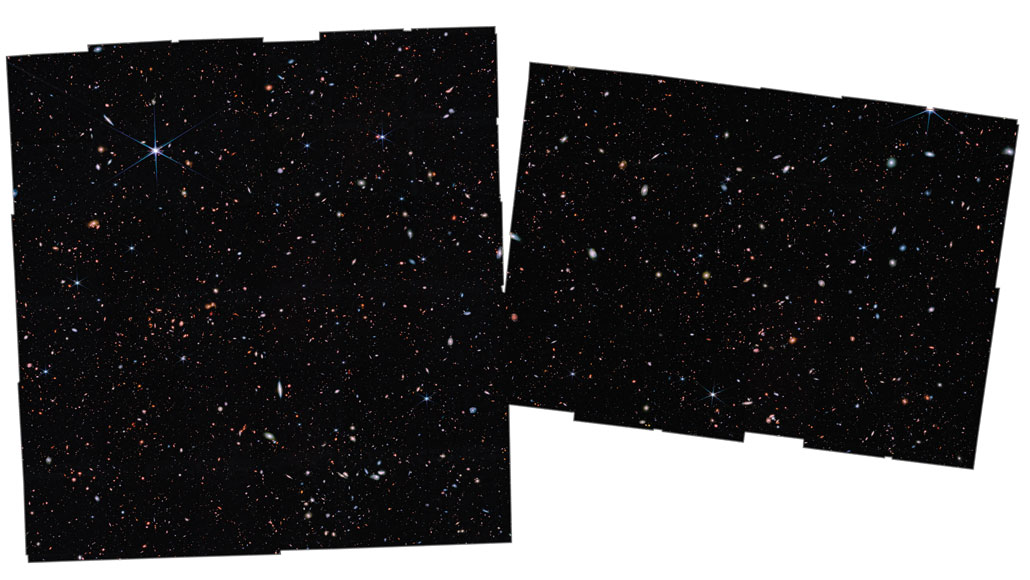
For longtime galaxy hunters, JWST’s bounty might really feel like déjà vu. Within the Nineteen Nineties, Hubble took a protracted, deep have a look at an it appears clean patch of sky, simply to look what used to be there. The end result used to be hundreds of galaxies, some captured as they appeared when the universe used to be just a billion years previous.
The ones galaxies appeared mature, like they’d already been via more than one rounds of supernova explosions and famous person formation. Thus, they weren’t the primary to shape within the universe, astronomers discovered. The primary galaxies should date even additional again.
The search for the ones unique galaxies used to be a part of the inducement for construction JWST, says astrophysicist Erica Nelson of the College of Colorado Boulder. “The rationale we now have JWST is, they introduced Hubble and noticed that the issues within the early universe had been very developed,” she says. “They had been like, ‘Wow! There are galaxies approach previous than we concept’ ” — even additional again in time than Hubble can see.
Hubble wasn’t designed to look the entire as far back as the universe’s starting. The telescope is delicate to ultraviolet, visual and near-infrared wavelengths of sunshine. However by the point gentle from the universe’s early days reaches us, it has stretched the entire approach into infrared wavelengths which are longer than Hubble’s (or human) eyes can see. That’s since the universe is increasing; the whole thing in it’s transferring clear of the whole thing else. And as gentle resources transfer clear of us, their gentle stretches — the wavelengths of sunshine develop longer, or redder.
The volume of stretching of that gentle, referred to as the redshift, is astronomers’ proxy for cosmic distance and age. The prevailing-day universe is at redshift 0. A redshift of one corresponds to about 6 billion years after the Giant Bang. A redshift of four is ready 1.5 billion years after the Giant Bang, and so forth.
In 1995, redshift 4 used to be the furthest again that Hubble may stumble on. Over the following twenty years, upgrades to the telescope and new staring at ways driven the frontier again to redshift 7, which corresponds to 800 million years after the Giant Bang. In 2012, the galaxy that Robertson studied gave the impression at a imaginable, regardless that on the time unconfirmed, redshift of eleven.9. Later, a galaxy known as GN-z11 clocked in at a redshift of eleven.1, or 400 million years after the Giant Bang.
Those tantalizing discoveries activate a seek for much more far-off galaxies. “This has roughly develop into a recreation in extragalactic astronomy, the place everybody needs to seek out the best possible redshift, maximum far-off galaxy,” astrophysicist Jeyhan Kartaltepe of the Rochester Institute of Era in New York stated in April in Minneapolis at an American Bodily Society assembly. “Grow to be the brand new checklist holder, proper? It’s amusing.”
Through 2016, when GN-z11 used to be found out, the quest had stalled. Astronomers had wrung the whole thing they may out of current era.
“It actually calls for JWST to push to even previous instances,” Kartaltepe stated, “which we wish to perceive the very beginnings of galaxy formation.”

Why astronomers wish to to find early galaxies
The hunt to seek out the earliest galaxies is ready extra than simply bragging rights. Those galaxies may make clear a key match within the universe’s infancy known as reionization.
At first, there used to be the Giant Bang. After that preliminary cataclysm, the universe persisted to make bigger and funky. After about 372,000 years, it had cooled sufficient for electrons, protons and neutrons to mix into hydrogen atoms. That hydrogen fuel used to be diffuse and opaque, plunging the universe into what astronomers name the cosmic darkish ages.
Someday right through those darkish ages, the primary stars shaped and started to clump in combination into galaxies with the assistance of an invisible and nonetheless mysterious subject material referred to as darkish topic. However on account of the opacity of that impartial hydrogen, all astronomers can actually apply is that the universe was clear once more at about 200 million years after the Giant Bang, as hydrogen atoms misplaced their electrons.
Subscribe to Science Information
Get nice science journalism, from essentially the most relied on supply, delivered to the doorstep.
“We all know there used to be a transition the place the hydrogen used to be reionized someway,” Robertson says. Due to observations with Hubble and different telescopes, “we expect galaxies are very most likely the brokers of that procedure,” he says. Mild from the youngest, maximum huge stars in the ones early galaxies may have knocked electrons off atoms within the hydrogen fuel between galaxies. “However how that procedure unfolds, we now have rather little knowledge on,” Robertson says.
JWST can assist fill in the ones main points. Taking a census of the galaxies that had been round right through the generation of reionization may assist remove darkness from the way it were given began.
And so, astronomers had been giddy with pleasure when JWST introduced on Christmas Day in 2021 and began amassing information about six months later. The primary photographs had been unveiled with nice fanfare on July 12, 2022 (SN: 8/13/22, p. 30). However astronomers needed to wait till the next day to come to obtain the remainder of the information the telescope had obtained whilst getting up and working.
“We knew, someplace, on some laptop, our photons had been sitting there, looking ahead to us to look them,” Kartaltepe stated. “Once the information had been launched in July, we jumped on it and began inspecting.”
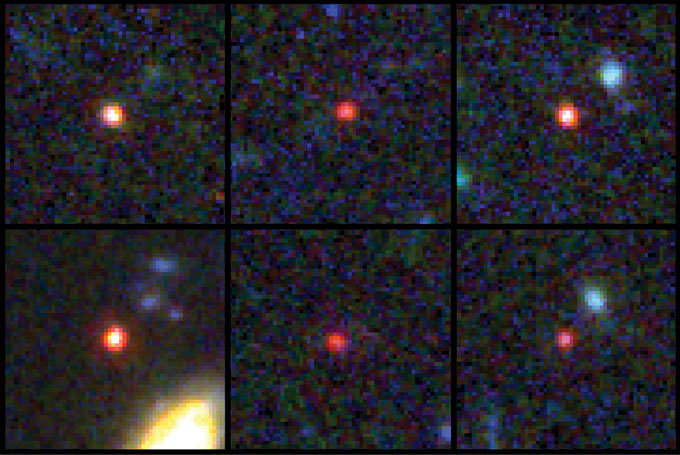
Astronomers sifted during the photographs like a cosmic The place’s Waldo, selecting the reddest-looking candidate galaxies out of the pack.
Extraordinarily far-off applicants popped out temporarily. In different other areas of the sky, JWST discovered little pink dots comparable to galaxies that gave the look to be at astonishing redshifts: 10, 13, even 17. Probably the most galaxies gave the impression small and dim, as anticipated. However others appeared giant and brilliant, suggesting they had been heftier than astronomers would be expecting for such early galaxies.
“Those galaxies, they’re simply at extra special distances. It’s a bit laborious to swallow,” Robertson stated in June in Cambridge, Mass., on the JWST First Mild Convention. “But it surely’s actually vital to in truth ascertain the distances to those very, very far-off galaxies, after which know about their homes.”
Probably the most far-off galaxy ever showed
Many of the cosmic distances reported for JWST galaxies thus far had been initial estimates according to information from the telescope’s cameras. The cameras scan vast spaces of sky and use filters to let in sure wavelengths of sunshine. Those filters permit astronomers to estimate “photometric” redshifts.
However to understand evidently how some distance away a galaxy actually is, astronomers wish to use JWST’s spectrograph. A redshift calculated from a galaxy’s complete spectrum of sunshine makes use of 1,000 information issues when put next with a photometric redshift’s seven information issues.
“Till we now have spectra, not anything is ironclad,” Nelson says.
As a part of a mission known as the JWST Complicated Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, Robertson and co-workers gathered spectra for 4 galaxies with photometric redshifts upper than 10 — most likely on the subject of the start of the generation of reionization. Probably the most galaxies used to be the only Robertson studied in 2012. The gap of that galaxy, now referred to as JADES-GS-z11-0, used to be downgraded somewhat, from a redshift of eleven.9 to 11.58. However with one of the most different galaxies, the group claimed a brand new checklist for many far-off galaxy ever showed, with a redshift of 13.2, simply 325 million years after the Giant Bang.
The spectra the group analyzed had been detailed sufficient to expose some homes of the galaxies, Robertson and co-workers reported in April in Nature Astronomy. They’re all a few hundredth the dimensions and mass of the Milky Means, however they’re forming stars at a related price — numerous stars for galaxies this small. All the ones new child stars produce numerous ionizing radiation, that means it’s imaginable those galaxies may well be one of the most earliest brokers of reionization, Robertson says.
JADES has since reported about 700 extra galaxies whose photometric redshifts position them at redshift 8 or better, or lower than 650 million years after the Giant Bang, Robertson stated on the June First Mild assembly. The ones galaxies’ distances nonetheless wish to be showed, however the sheer numbers are wonderful. “We’re actually in a exceptional age,” Robertson stated.
Trusting JWST’s measurements
The massive galaxy haul raises any other query: What number of of them usually are at such nice distances?
A possible record-breaking galaxy known as CEERS-93316 is a cautionary story. The galaxy used to be known in JWST photographs taken for the Cosmic Evolution Early Unencumber Science, or CEERS, survey. The ones photographs put the galaxy at a photometric redshift of 16.4, or simply 240 million years after the Giant Bang.
“That used to be upper redshift than we anticipated to look with CEERS,” says Finkelstein, the survey’s lead researcher. CEERS used to be designed to apply the usage of JWST in its other staring at modes and provides astronomers some information to play with, now not essentially to set new information.
In its first bite of knowledge, CEERS contained a stunning selection of it appears high-redshift galaxies. So Finkelstein and co-workers requested the director of the House Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, which operates JWST, for some additional telescope time to chase down the spectra of CEERS-93316, in addition to a galaxy that Finkelstein had discovered with a photometric redshift of about 12. He named that galaxy Maisie’s Galaxy in honor of his daughter, as a result of he discovered it on her 9th birthday. (Maisie didn’t thoughts that her dad needed to paintings that day — “I were given different birthday gifts,” she says, regardless that she did want her galaxy used to be the possible checklist holder.)
When the spectral information got here via, Finkelstein’s colleague Pablo Arrabal Haro, an astrophysicist on the Nationwide Science Basis’s NOIRLab, primarily based in Tucson, labored during the weekend to write down up effects sooner than somebody else.
CEERS-93316’s 16.4 redshift became out to be improper. The galaxy used to be in truth at a redshift of four.9, placing it 1.2 billion years after the Giant Bang — almost fashionable when put next with a few of JWST’s different reveals.
The galaxy’s photometric redshift used to be so excessive on account of a peculiar accident. Mild streaming from hydrogen within the galaxy used to be redshifted such that it appeared adore it jumped in brightness at a wavelength suggestive of the large distance. But if the whole spectrum got here in, that unmarried leap used to be published to be a number of separate peaks, suggesting a smaller redshift.
Maisie’s Galaxy, alternatively, is virtually as far-off because the photometric redshift implied, Arrabal Haro and co-workers reported in a paper posted in March to arXiv.org. And in an April paper posted to arXiv.org, the group reported spectra for greater than 30 different galaxies with redshifts of more or less between 8 and 10. So photometric redshift estimates are usually dependable, Finkelstein says.
“Even if we now have this notable failure case, that’s a pathological case,” he says. It’s “now not devastating.”
That’s excellent information for JWST’s staring at agenda: Astronomers gained’t need to apply up with the whole spectrum for each far-off galaxy. They are able to consider that many of the redshifts are respectable and save the additional effort of taking the whole spectrum for the actually fascinating ones. “It’s thrilling that the photometric redshifts have a tendency to carry up,” Robertson says. “It offers us some hope that a few of these actually far-off issues may well be actual.”
Far-off galaxies too brilliant to provide an explanation for
Every other consequence of JWST analyses thus far is that there are extra brilliant galaxies round redshift 10 than anticipated. Galaxy brightness is a trademark of galaxy mass, and thus famous person abundance. The brighter the galaxy, the extra stars it should have to supply all that gentle.
Galaxies are born in halos of darkish topic, whose gravity pulls in and concentrates abnormal topic. Cosmologists know from simulations and principle what number of darkish topic halos the universe would have had when the primary galaxies shaped. They even have a respectable concept of ways huge the ones halos had been within the universe’s first 500 million years and what sort of of that mass ended up within the type of hydrogen and helium, the uncooked subject material for making stars. Theoretically, if all that fuel changed into stars, the biggest a galaxy may get could be about 10 billion instances the mass of the solar.
Actually, researchers be expecting early galaxies to be a lot much less huge, as a result of fashionable galaxies by no means convert all their fuel into stars.
JWST has now not became up any galaxy close to the theoretical higher prohibit. But it surely has discovered many extra hefty early galaxies than predicted. The showed JADES galaxies weigh in at about 100 million sun lots, simply 330 million years after the Giant Bang. Probably the most CEERS galaxies appear to have over one billion suns’ value of stars as early as 450 million years after the Giant Bang. Two galaxies found out in any other JWST survey, known as COSMOS-Internet, seem to be about 5 billion sun lots as early as 350 million years after the Giant Bang, astronomer Caitlin Casey of the College of Texas at Austin stated on the June First Mild assembly.
“With those huge beacons, you’ll take a look at the bounds of ways rapid you’ll collect that a lot topic within the short while between the Giant Bang and the time that we’re staring at them in,” she says.
What astronomers to find from those galaxies may level to the place our current working out of galaxy formation is improper. Or researchers may uncover that one of the most galaxies’ gentle doesn’t come without delay from stars however as an alternative from the ionized fuel in between stars which are actively forming, Casey says. That might imply the galaxies aren’t in truth as huge as they give the impression of being.
Learning how early galaxies had been put in combination is step one to working out our personal galaxy, Robertson says. “That’s in the end what drives numerous galaxy formation analysis, is making an attempt to know how our house, the article that’s vital to us, where that we are living, got here to be,” he says. “We’re by no means going to finish that complete tale with out searching at how galaxies at redshift 10 had been put in combination…. That’s the beginning position for a way we were given right here.”
Breaking the universe … or now not
One set of galaxies has sparked debate over now not simply galaxy formation, however the theoretical foundations of the universe itself.
In February, Nelson and co-workers reported six galaxies noticed with CEERS that appear to have grown so giant, so rapid that they without delay problem the usual principle of ways construction paperwork within the universe (SN: 3/25/23, p. 14). Those galaxies have photometric redshifts between about 7 and 9, that means they grew up within the first 800 million years of the universe. However their stellar lots seem to rival or exceed that of the Milky Means, about 60 billion sun lots.
Nelson affectionately calls them the “universe breakers.” Not anything that vast must had been in a position to shape that rapid, she says. “Once we noticed it, we had been like, that is bananas.”
Slightly sufficient abnormal topic is even believed to have existed again then to create the universe breakers, says astrophysicist Mike Boylan-Kolchin of the College of Texas at Austin. Areas the place budding galaxies shaped would have needed to flip all their atoms into stars.

“We now have this reservoir of atoms,” he says. “Nearly each unmarried considered one of them must be in stars or in galaxies” if the universe breakers are for actual. “If those observations and their interpretation is right kind … it’s very laborious to house them in our present fashions,” he says.
Over the previous few months, theorists have get a hold of a number of tactics to provide an explanation for the universe breakers. Some of the dramatic choices could be so as to add some additional darkish power, the mysterious substance that drives the universe to make bigger quicker and quicker, to the early universe, which might accelerate all varieties of cosmic processes.
“That might pass in the proper course right here, within the sense that there’d be larger reservoirs [of atoms] and perhaps extra of them at previous instances,” Boylan-Kolchin says. “Those early darkish power fashions do are expecting quicker evolution of construction at early instances.”
Extra mundane choices come with super-compact early galaxies that will have transformed all their fuel into stars sooner than the oldest stars had an opportunity to move supernova and blow it away. Such environment friendly famous person formation may give an explanation for the universe breakers with out breaking the universe, physicist Avishai Dekel of the Hebrew College in Jerusalem and co-workers urged in a paper revealed Would possibly 25 within the Per month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
And there’s nonetheless the query of whether or not the universe breakers’ lots and distances will grasp up. A spectrum of considered one of them has already published it to be a galaxy at redshift 5.6 with an actively feeding black hollow growing additional gentle — so now not a universe breaker finally.
JWST’s 2nd staring at cycle started in July, and Nelson will take spectra of the remainder of the universe breakers to determine if they’re really abounding with stars, stuffed with black holes or one thing else.
In the meantime, any other workforce of astronomers will take a look at JWST’s limits, looking for galaxies at redshift 15 or better. So through the telescope’s 2nd birthday subsequent summer season, there could also be new distance information.
