Assays to be had
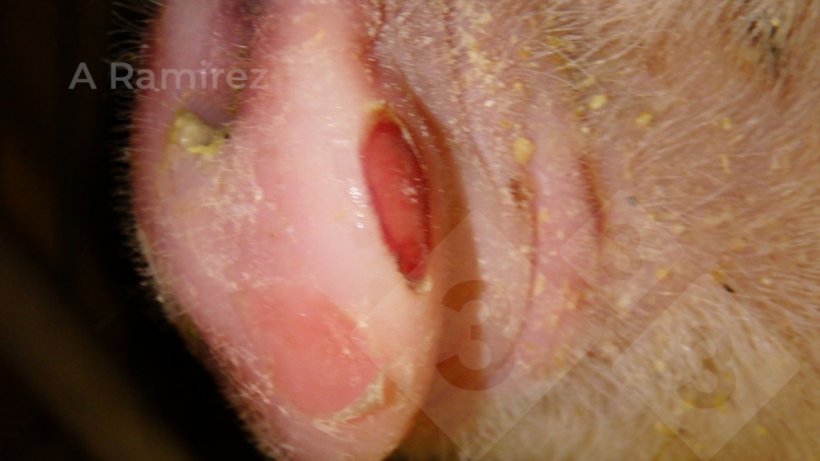
Gross pathology
- Id of lesions particularly vesicles in snout and ft spaces
- Execs:
- Simple to spot vesicles grossly
- Cons:
- Clinically indistinguishable from all different vesicular sicknesses
- Normally require different diagnostic affirmation
Polymerase chain response (PCR)

- Detects presence of particular collection of viral nucleic acid (RNA)
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most well-liked pattern form), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium no longer to be had), milk
- Execs:
- Maximum delicate and most well-liked manner for detecting agent
- Can ceaselessly do pooling of samples to cheaper price whilst minimizing lack of sensitivity
- Can goal common proteins for basic detection or serotype particular proteins for serotyping
- Cons:
- Average price
- Calls for correct primers particularly if concentrated on structural proteins that are serotype particular
Record of recently identified serotypes for FMD (There’s no go coverage between serotypes):
- Asia 1
- South African Sort 1 (SAT 3)
- South African Sort 1 (SAT 2)
- South African Sort 1 (SAT 1)
- C
- A
- O
Antigen Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Ag-ELISA)
- Detects presence of antigen
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most well-liked pattern form), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium no longer to be had), milk
- Execs:
- Most popular manner for detection and identity of serotype
- Can be utilized at a person animal or herd stage prognosis
- Can be utilized to distinguish serotypes
- Any sure end result to wild-type virus is thought of as vital
Desk 1. Other viral proteins can be utilized to lend a hand with diagnostic objectives.
| Goal antigen | Variability | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Structural proteins | Variable | Serotyping |
| Non-structural proteins | Conserved | Common detection: None-Serotype particular |
- Cons:
- Presence of viral antigen could also be serotype particular
- Might wish to do more than one assessments to spot serotypes
Antibody Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Ab-ELISA)
- Detects presence of antibodies
- Pattern sorts: serum
- Execs:
- Circulating antibodies will also be detected once 3-5 days after scientific indicators famous
- Animals stay sure for a number of months
- Can be utilized in older instances
- Can be utilized to distinguish publicity to wild-type from some killed/recombinant vaccines (goal particular non-structural proteins)
- Any sure end result to wild-type virus is thought of as vital
- Cons:
- Antibody reaction is serotype particular
- Some animals would possibly keep seropositive for a number of years
- Power of immune reaction would possibly range with virulence of pressure
- Presence of antibodies does no longer at all times correlate with coverage
Lateral waft units (LFD)
- Detects presence of antigen
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium
- Execs:
- Most popular manner for detection and identity of serotype
- Can be utilized at a person animal or herd stage prognosis
- Can be utilized to distinguish serotypes
- Any sure end result to wild-type virus is thought of as vital
- Cons:
- Presence of viral antigen could also be serotype particular
- Much less delicate than Ag-ELISA
- Might wish to do more than one assessments to spot serotypes
Virus isolation (VI)
- Isolates reside virus
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most well-liked pattern form), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium no longer to be had), milk
- Execs:
- Conventional gold usual
- Isolate virus to be used in vaccine building (autogenous vaccines) or serology trying out (ELISA) to decide serotype.
Cons:
- Pricey
- Sluggish effects
- Calls for particular cellular strains; bovine (calf) thyroid cells or pig, calf, or lamb kidney cells
- Inoculation procedure is hard work extensive
- Steadily tough to develop (false negatives)
Genetic sequencing
- Sequences virus’s genetic nucleic acids (RNA)
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most well-liked pattern form), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium no longer to be had), milk
- Execs:
- Can lend a hand with molecular epidemiology
- Lend a hand determine serotype
- Cons:
- Pricey
- Sluggish to get effects
Outcome interpretation
Gross Lesions (vesicles)
- Certain: Should examine as imaginable FMD
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable or ignored if trying out happens past due after an infection or inflamed with a light pressure
PCR
- Certain: Virus is provide
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable or virus will have been ignored if trying out happens past due after an infection
Ag-ELISA
- Certain: Virus is provide
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable, virus will have been ignored if trying out happens past due after an infection, or examined for incorrect serotype
Ab-ELISA
- Certain: Maternal antibodies or previous publicity (>2-3 days) to wild-type virus or some vaccines
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable or publicity to vaccine or wild-type virus too early to locate, or examined for incorrect serotype antibody
LFD
- Certain: Virus is provide
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable, virus will have been ignored if trying out happens past due after an infection, or examined for incorrect serotype
VI

- Certain: Virus is provide
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable, virus will have been ignored if trying out happens past due after an infection, or incorrect cellular line used
Genetic Sequencing
- Certain: Virus is provide
- Unfavourable: Unfavourable, virus will have been ignored if trying out happens past due after an infection, or too little virus provide for sequencing
Situations
It is very important word that some international locations would possibly require approval by means of federal government earlier than any trying out for FMD will also be accomplished.
Suspected acute FMD outbreak in any age pigs and herd no longer vaccinated for FMD
- Acquire vesicular fluid from more than one affected animals and check by way of Ag-ELISA or PCR; for PCR pattern pooling could also be regarded as
Suspected acute FMD outbreak in any age pigs and herd vaccinated for FMD
- Acquire vesicular fluid from more than one affected animals and check by way of Ag-ELISA or PCR; for PCR pattern pooling could also be regarded as
- Acquire serum from more than one affected animals that experience proven scientific indicators for a minimum of 3 days and check for my part by way of Ab-ELISA; goal non-structural protein that isn’t found in vaccine
Suspicion of FMD circulate in any age pigs without a scientific indicators and herd isn’t vaccinated for FMD
- Acquire serum from 30 randomly sampled pigs and check for my part by way of Ab-ELISA; goal structural protein
Suspicion of FMD circulate in any age pigs without a scientific indicators and herd is vaccinated for FMD
- Acquire serum from 30 randomly sampled pigs and check for my part by way of Ab-ELISA; goal none-structural protein that isn’t found in vaccine
