We all know atrophic rhinitis (AR) as a illness characterised through deformation. of the snout. This deformation effects from an irreversible contraction (atrophy) of the nasal turbinates, led to through toxins produced through two micro organism: Pasteurella multocida sort D and Bordetella bronchiseptica.
B. bronchiseptica, the bacterium
Bordetella bronchiseptica is a in style bacterium on our swine farms. Its toxicity is because of the irritation of the mucosal lining of the nostril and lungs that generates however incessantly it produces additionally gentle lesions within the type of a short lived atrophy of the nasal turbinates. This implies an infection because of B. bronchiseptica is incessantly overpassed since the lesions are temporary and reversible. An experimental find out about through which four-day-old piglets had been inflamed with the bacterium, confirmed through CT scan of the snout, that probably the most critical atrophy of the turbinates happens round six weeks of age, and then, the turbinates go back to their authentic construction and no lesions are noticed on the slaughterhouse. Because the prognosis of atrophic rhinitis is incessantly made through chopping the snout on the slaughterhouse, the non-progressive type of atrophic rhinitis will also be overpassed.once more.

The have an effect on of B. bronchiseptica is going past macroscopic lesions as slso the cilia within the trachea are affected. Those cilia are accountable for eliminating the international components and germs from the frame and raise them into the throat so they don’t succeed in the deeper breathing machine. Thus, an infection with B. bronchiseptica makes animals extra prone to different pathogens.
The most efficient-known instance is an infection through Pasteurella multocida sort D, a bacterium that on its own does now not possess the power to colonize the breathing tract however earlier colonization through B.bronchiseptica facilitates next colonization through Pasteurella multocida sort D.
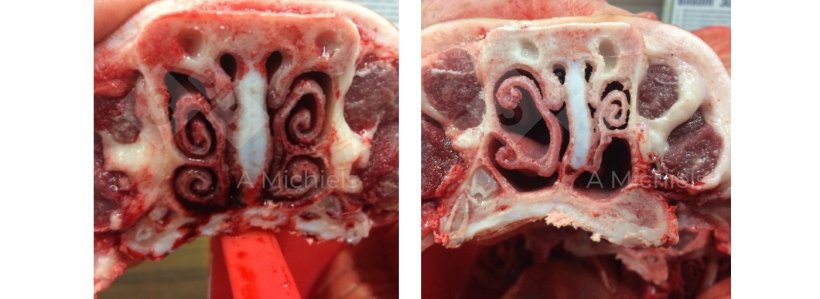
Determine 1. Left: A pig with wholesome turbinates the place the nostril is the primary clear out to battle the access of breathing pathogens. Proper: turbinates suffering from non-progressive atrophic rhinitis. The snout twists, shrinks and wrinkles. Piglets display now and again even nasal bleeding.
Bordetella bronchiseptica as a predisposing issue: past co-infection with Pasteurella
B. bronchiseptica will act as an opportunistic pathogen, contributing to porcine breathing illness complicated (PRDC). Because of its pathogenesis, it produces a short lived atrophy of the nasal turbinates and impacts the breathing cilia of piglets all the way through the nursery segment, facilitating the access into the organism: of pathogens comparable to the next:
- Gläesserella parasuis (explanation for Glässer illness)
- Streptococcus suis
- PRRS virus
- Influenza virus
Subsequently, coverage in opposition to B. bronchiseptica can cut back the chance of more than a few breathing infections and lend a hand animals struggle them higher.
B. bronchiseptica and its affect on Streptococcus
Microorganisms that purpose number one breathing issues aren’t the one ones that have the benefit of the trail cleared through B. bronchiseptica. Streptococcus suis (S. suis) additionally has a unfastened trail when B. bronchiseptica has performed its process destroying the turbinates, the primary barrier to coming into the breathing machine.
So as to cut back antibiotic use, regulation and manufacturing firms have put more than a few measures in position to restrict their use. Sadly, this additionally manner restricting some of the gear that can be utilized to stop Streptococcus issues at the farm. Subsequently, along with making improvements to piglet high quality at weaning, biosecurity, and control, we should search for choice the way to save you Streptococcus an infection. Vaccinating in opposition to B. bronchiseptica is helping cut back S. suis-associated mortality through decreasing the possibility of S. suis having access to the piglet.
Case find out about
On a industrial farm in Europe, with a prime mortality fee because of meningitis and arthritis, S. suis used to be remoted a number of occasions from meninges and joints. To keep watch over the medical indicators, the farm maintained regimen drugs with amoxicillin within the water. B. bronchiseptica used to be found in oral fluids however P. multocida toxin used to be now not discovered. Since earlier experiences level to the keep watch over of secondary infections by means of the keep watch over of B. bronchiseptica, it used to be determined to analyze the affect of vaccination in opposition to non-progressive atrophic rhinitis within the prevention of S. suis an infection. For this goal, the next piglet teams had been adopted in parallel through the years:
- 3 batches from sows vaccinated with a vaccine in opposition to non-progressive atrophic rhinitis
- 3 batches from non-vaccinated sows (keep watch over staff)
Regimen use of amoxicillin in water used to be discontinued all the way through the trial.
Effects
A transparent relief within the presence of B. bronchiseptica within the oral fluids of piglets at 5 and eight weeks of age used to be noticed in piglets from vaccinated sows (Determine 2).
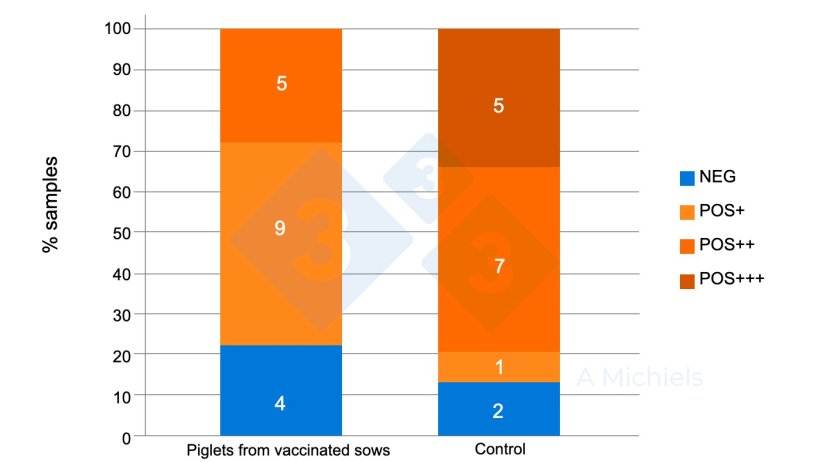
Determine 2. Oral fluid samples from 5- and 8-week-old piglets. Piglets from vaccinated dams (left) display a robust relief within the incidence of B. bronchiseptica in comparison to effects from the unvaccinated keep watch over staff (proper).
This relief within the presence of B. bronchiseptica in oral fluids correlates with a 79% relief in mortality because of meningitis in piglets within the vaccinated staff. As well as, the full choice of antibiotic therapies in line with 100 piglets used to be decrease within the vaccinated staff in comparison to the non-vaccinated staff.
Desk 1. Piglets from vaccinated sows vs. piglets from unvaccinated sows. Parameters with an (*) had been considerably other inside of a column.
| Team | Weaned piglets | Nursery mortality (%) | Antibiotic use for each and every 100 animals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | Meningitis | Diarrhea | Meningitis | ||
| Vaccinated | 3,209 | 2.13 | 0.07* | 18.78* | 0.25 |
| No longer vaccinated | 2,820 | 2.49 | 0.34 | 25.49 | 0.47 |
This farm diminished the prevalence of S. suis-associated mortality through vaccinating in opposition to non-progressive atrophic rhinitis. It’s important, due to this fact, to decide if B. bronchiseptica is provide at the farm, as lesions led to through this bacterium incessantly move omitted.
