The canine days of summer time are upon us. Brutal warmth waves are roasting areas around the world, smashing information with unrelenting severity.
Within the southwest United States and northerly Mexico, devastating warmth has been sizzling the area for weeks. For 19 immediately days and counting, temperatures in Phoenix have reached above 43.3° Celsius (110° Fahrenheit), surpassing a file streak from 1974. The Texas town of El Paso has continued an remarkable 33 consecutive days of temperatures achieving over 37.8° C (100° F), and that streak is handiest anticipated to proceed. And simply after middle of the night on July 17, Dying Valley, Calif., will have sweltered below the easiest temperature ever recorded anyplace for that point: 48.9° C (120° F).
China has additionally been enduring excessive warmth for weeks. On July 16, the township of Sanbao broke now not handiest the nationwide file with a temperature of 52.2° C (126° F), but in addition the file for easiest temperature above 40˚ N latitude. In the meantime, southern Europe is in its 2nd warmth wave in every week, with Rome recording a brand new all-time excessive of 42.9° C (109.2° F) on July 18 whilst a the city in Catalonia, Spain set a brand new file for the area, 45.3° C (113.5° F).
What’s concocting those bouts of utmost warmth? It’s in part since the international has been exceptionally heat this yr, because of the compounding of human-caused weather exchange with a herbal weather phenomenon known as El Niño, whose affect is understood to quickly heat our planet (SN: 7/13/23).
But it surely’s now not simply that Earth’s a warmer stovetop; the chefs were busy. The jet streams, robust ribbons of wind that regulate a lot of the planet’s climate, were meandering and getting caught, retaining bulges of scorching air over many portions of the Earth. Whilst that’s now not strange, some scientists have advised that weather exchange is also changing the dynamics of the consequential winds.
Right here’s what we find out about how weather exchange is impacting excessive warmth and the way those probably bad occasions happen.
Excessive warmth waves are changing into much more likely
Let’s get started with that scorching stovetop. People were warming the planet for many years by way of emitting climate-warming greenhouse gases into the ambience. That’s made excessive warmth waves extra commonplace, many researchers say.
Since 2004, scientists have performed attribution research to estimate how a lot weather exchange will have influenced the likelihood and severity of a selected bout of utmost climate. Those research necessarily simulate the arena with and with out weather exchange to match how steadily positive varieties of excessive climate occasions happen.
The paintings of the International Climate Attribution initiative has again and again indicated that weather exchange has made excessive climate occasions like warmth waves much more likely and extra serious (SN: 4/11/22; SN: 7/7/21).
A Might record concluded that an April warmth wave in South Asia — throughout which places in Thailand and Laos set new nationwide temperature information of 45.4° C and 42.9° C, respectively — was once made a minimum of 30 occasions much more likely because of weather exchange.
Any other learn about advised {that a} other warmth wave in northern Africa and southwestern Europe, which subjected some spaces to temperatures 20 levels C upper than is customary in April, was once a minimum of 100 occasions much more likely because of weather exchange.
Local weather exchange is pushing warmth waves typically to have upper temperatures, nevertheless it’s having a specifically robust affect at the frequency of probably the most excessive occasions, says atmospheric scientist Noboru Nakamura of the College of Chicago.
“What was once as soon as each and every 1,000 years may now happen each and every two decades,” he says. “It’s nonetheless an extraordinary match, however … you’ll in reality really feel that during our day by day lives.”
How warmth waves type
What’s in reality whipping up those summer time scorchers, and why are handiest positive areas getting roasted?
The solution lies kind of 8 to fourteen kilometers excessive within the sky. There, the jet streams waft at about 177 kilometers in keeping with hour on reasonable, even though they may be able to succeed in speeds of greater than 400 kilometers in keeping with hour — sooner than a Shinkansen bullet educate.
Those robust winds regulate a lot of Earth’s climate by way of transporting high- and low-pressure techniques around the globe.
Jet streams increase the place massive lots of air with other temperatures meet, flowing sooner the place the temperature distinction is more potent. When jet streams are blowing robust, they have a tendency to orient themselves extra parallel to the equator, says atmospheric scientist Jennifer Francis of the Woodwell Local weather Analysis Heart in Falmouth, Mass. “But if the ones winds get weaker … then we have a tendency to look the jet movement take those larger meanders.”
When the jet movement meanders, it paperwork huge waves, with crests and troughs that stretch north and south for masses of kilometers. Jet streams within the northern and southern hemispheres in most cases undulate extra throughout their respective summers. Because of Earth’s axial tilt, polar areas obtain extra warming daylight throughout their summers, weakening their temperature distinction with the tropics. Because the waves develop into amplified, high- and low-pressure techniques within the crests and troughs encroach farther north and south. Once in a while those stress techniques develop into caught over one spot for days to weeks, inflicting climate to persist over a area.
When a high-pressure gadget will get caught over a space, it pushes air down towards the skin, compressing and warming the air. The excessive stress additionally pushes clouds away, clearing the sky for the recent solar to overcome down unabated. Those elements compound to supply a warmth dome, a phenomenon that scorches and steadily dries landscapes.
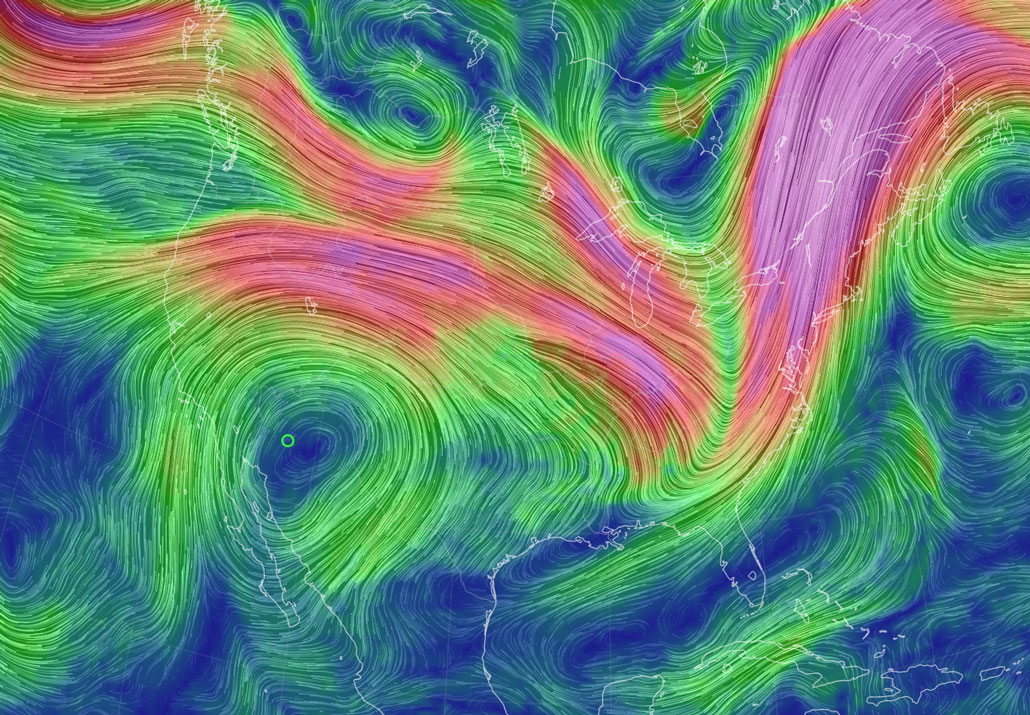
Supply: GFS/NCEP/NOAA
An exception is when warmth domes type by way of coastlines — comparable to the one who has shaped by way of the U.S. Gulf Coast. Since hotter air can elevate extra moisture, warmth domes close to the sea could make for climate this is each scorching and humid, a probably deadly aggregate for people (SN: 7/27/22).
It’s somewhat of a thriller why stress techniques develop into caught, Nakamura says, making the phenomenon tough to are expecting. It’s going to happen when jet streams develop into particularly wavy, he and a colleague reported in 2018 in Science. The waves would possibly get caught like automobiles in a visitors jam, inflicting climate to idle in position.
However this clarification is a theoretical one, and extra proof is had to validate it, Nakamura says. Till then, he says, the underlying mechanics of the ones jams will stay elusive.
The jet streams’ unsure long term
A comparable, however in a similar way unresolved, drawback is how weather exchange would possibly have an effect on the dance of the jet streams one day. In 2012, Francis and a colleague proposed weather exchange may just make the robust winds extra wobbly.
“The Arctic is warming about 4 occasions sooner than the globe as a complete,” Francis says. “That implies that the north-south temperature distinction has been getting weaker and weaker.” In consequence, jet streams is also changing into extra risky, she says, and extra at risk of meandering.
However that’s nonetheless “an excessively hotly contested speculation,” Nakamura says, declaring that some weather simulations have advised that within the Northern Hemisphere, the jet movement would possibly in reality develop into much less wavy. “There isn’t a broadly authorised consensus in this,” Nakamura says.
Even though the destiny of the jet streams stays up within the air, something turns out transparent: Excessive warmth waves aren’t going anyplace.
